GCP – Driving diversity in AI: a new Google for Startup Accelerator for Women Founders from Europe & Israel
Post Content
Read More for the details.

Post Content
Read More for the details.
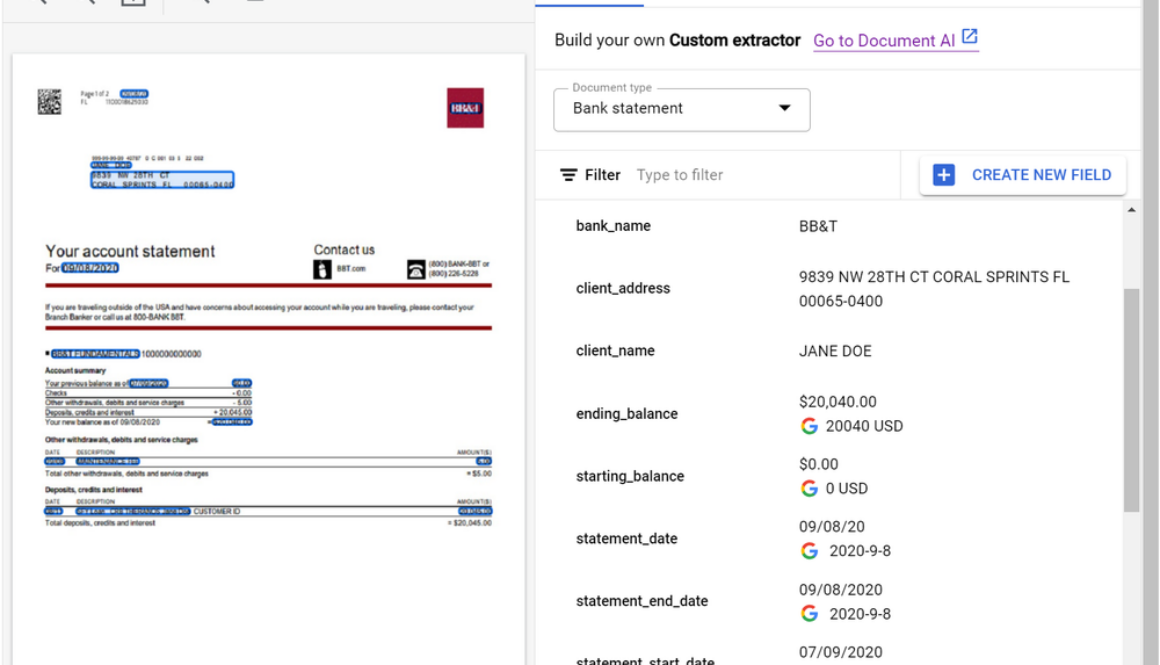
Today, we are excited to announce that the Document AI Custom Extractor, powered by generative AI, is Generally Available (GA), open to all customers, and ready for production use through APIs and the Google Cloud Console. The Custom Extractor, built with Google’s foundation models, helps parse data from structured and unstructured documents quickly and with high accuracy.
In the past, developers trained discrete models by using thousands of samples for each document type and spending a significant amount of time to achieve production-ready accuracy. In contrast, generative AI enables data extraction from a wide array of documents, with orders of magnitude less training data, and in a fraction of the time.
In spite of the benefits of this new technology, implementing foundation models across document processing can be cumbersome. Developers need to manage facets such as converting documents to text, managing document chunks, optimizing extraction prompts, developing datasets, managing model lifecycles, and more.
Custom Extractor, powered by generative AI, helps solve these challenges so developers can create extraction processors faster and more effectively. The new product allows for foundation models to be used out of the box, fine tuned, or used for auto-labeling datasets through a simple journey. Moreover, generative AI predictions are now covered under the Document AI SLA.
The result is a faster and more efficient way for customers and partners to implement generative AI for their document processing workflows. Whether to extract fields from documents with free-form text (such as contracts) or complex layouts (such as invoices or tax forms), customers and partners can now use the power of generative AI at an enterprise-ready level. Developers can simply post a document to an endpoint and get structured data in return with no training required.
During public preview, developers cut time to production, obtained higher accuracies, and unlocked new use cases like extracting data from contracts. Let’s hear directly from a few customers:
“Our partnership with Google Cloud continues to provide innovative solutions for Iron Mountain’s Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) and Workflow Automation capabilities powered by Iron Mountain InSight®. Document AI’s Custom Extractor enables us to leverage the power of generative AI to classify and extract data from unstructured documents in a faster and more effective way. By using this new product and with features such as auto-labeling, we are able to implement document processors in hours vs days or weeks. We are able to then build repeatable solutions, which can be delivered at scale for our customers across many industries and geographies.” – Adam Williams, Vice President, Head of Platforms, Iron Mountain
“Our collaboration with Google marks a transformative leap in the Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) space. By integrating Google Cloud’s Document AI Custom Extractor with Automation Anywhere’s Document Automation and Co-Pilot products, we’re leveraging generative AI to deliver a game-changing solution for our customers. With the integration of the Custom Extractor, we are not just improving document field extraction rates; we are also accelerating deployment time by more than 2x and cutting ongoing system maintenance costs in half. We are excited to partner with Google to shape the next generation of Intelligent Document Processing solutions and revolutionize how organizations automate document-intensive business processes.” – Michael Guidry, Head of Intelligent Document Processing Strategy, Automation Anywhere
In addition, the latest Workbench updates make it even easier to automate document processing:
Price reduction- to better support production workloads, we reduced prices with volume-based tiers for Custom Extractor, Custom Classifier, Custom Splitter, and Form Parser For more information, see Document AI pricing.Fine tuning – Custom Extractor supports fine-tuning (Preview) so you can take accuracy to the next level by customizing foundation model results for your specific documents. Simply confirm extraction results within a dataset and fine-tune with a click of a button or an API call. This feature is currently available in the US region. For more information, see Fine tune and train by document type.Expanded region availability: predictions from the Custom Extractor with generative AI are now available in the EU and northamerica-northeast1 regions. For more information, see Custom Extractor regional availabilty.Version lifecycle management: As Google improves foundation models, older foundation models are deprecated. Similarly, older processor versions will be deprecated 6+ months after new stable versions are released. We are working on an auto-upgrade feature to simplify lifecycle management. For more information, see Managing processor versions.
To quickly see what the Custom Extractor with generative AI can do, check out the updated demo on the Document AI landing page. Simply load a sample document (15 page demo limit). In seconds you will see the power of generative AI extraction as shown below.
If you are a developer, head over to Workbench on the Google Cloud Console to create a new extractor and to manage complex fields or customize foundation models’ predictions for your documents.
Or, to learn more, review documentation for the Custom Extractor with generative AI, review Document AI release notes, or learn more about Document AI and Workbench.
Read More for the details.

BigQuery makes it easy for you to gain insights from your data, regardless of its scale, size or location. BigQuery Data Transfer Service (DTS) is a fully managed service that automates the loading of data into BigQuery from a variety of sources. DTS supports a wide range of data sources, including first party data sources from the Google Marketing Platform (GMP) such as Google Ads, DV360 and SA360 etc. as well as cloud storage providers such as Google Cloud Storage, Amazon S3 and Microsoft Azure.
BigQuery Data Transfer Service offers a number of benefits, including:
Ease of use: DTS is a fully managed service, so you don’t need to worry about managing infrastructure or writing code. DTS can be accessed via UI, API or CLI. You can get started with loading your data in a few clicks within our UI.Scalability: DTS can handle large data volumes and a large number of concurrent users. Today, some of our largest customers move petabytes of data per day using DTS.Security: DTS uses a variety of security features to protect your data, including encryption and authentication. More recently, DTS has added capabilities to support regulated workloads without compromising ease-of-use.
Based on customer feedback, we launched a number of key feature updates in the second half of 2023. These updates include broadening our support for Google’s first party data sources, enhancing the current portfolio of connectors to incorporate customer feedback and improve user experience, platform updates to support regulated workloads, as well as other important security features.
Let’s go over these updates in more detail.
Display and Video Ads 360 (DV360) – A new DTS connector (in preview) allows you to ingest campaign config and reporting data into BigQuery for further analysis. This connector will be beneficial for customers who want to improve their campaign performance, optimize their budgets, and target their audience more effectively.Azure Blob Storage – The new DTS connector for Azure Blob Storage and Azure Data Lake Storage (now GA) completes our support for all the cloud storage providers. This allows customers to automatically transfer data from Azure Blob Storage into BigQuery on a scheduled basis.Search Ads 360 (SA360) – We launched a new DTS connector (in preview) to support the new SA360 API. This will replace the current (and now deprecated) connector for SA360. Customers are invited to try the new connector and prepare for migration (from the current connector). The new connector is built using the latest SA360 API that includes platform enhancements as documented here.
Google Ads: Earlier in 2023, we launched a new connector for Google Ads that incorporated the new Google Ads API. It also added support for Performance Max campaigns.
Recently, we enhanced the connector with a feature (in preview) to enable customers to create custom reports that use a Google Ads Query Language (GAQL) query. Customers have to use their existing GAQL queries on configuring a transfer. With this feature, customers will have an optimized data transfer that pulls in just the data they need and at the same time bring in newer fields that might not be supported in a standard Google Ads transfer.
Additionally, we added support for Manager Accounts (MCC) with a larger number of accounts (8K) for our larger enterprise customers.YouTube Content Owners: Expanded support for YouTube Content Owner by increasing the coverage of CMS reports by adding 27 new financial reports. You can find the details of all the reports supported here.Amazon S3: Enabled hourly ingestion from Amazon S3 (vs. daily ingestion previously) to improve data freshness. This has been a consistent customer requested feature to improve the freshness of data from S3.
Your data is only useful if you can access it in a trusted and safe way. This is particularly important for customers running regulated workloads. To that end, we enabled:
Customer-managed encryption keys (CMEK) support for scheduled queries, Cloud Storage transfers, and Azure Blob Storage transfersService Account support for additional data sources: Campaign Manager, Teradata, Google Play, Amazon Redshift, Search Ads 360, and Display & Video 360.Data residency and access transparency controls for scheduled queries and Cloud Storage transfers.Enabled support for Workforce Identity Federation for all data sources except for YouTube Channel Transfers.
As we look to 2024, we are excited to continue this rapid innovation with new connectors for marketing analytics, operational databases and enterprise applications. At the same time, we look to evolve our portfolio of connectors with capabilities that improve the “freshness” of data, and help customers with AI-assisted transformations.
Try BigQuery Data Transfer Service today and streamline loading your data into BigQuery!
Read More for the details.
BigQuery is a powerful and scalable petabyte-scale data warehouse known for its efficient SQL query capabilities, and is widely adopted by organizations worldwide.
While BigQuery offers exceptional performance, cost optimization remains critical for our customers. Together, Google Cloud and Deloitte have extensive experience assisting clients in optimizing BigQuery costs. In a previous blog post, we discussed how to reduce and optimize physical storage costs when implementing BigQuery. This blog post focuses on optimizing BigQuery computational costs through the utilization of the newly introduced BigQuery editions instead of the on-demand ($/TB) pricing model.
Selecting BigQuery editions slots with autoscaling is a compelling option for optimizing costs.
Many organizations select BigQuery’s on-demand pricing model for their workloads due to its simplicity and pay-per-query nature. However, the computational query analysis costs can be significant. Minimizing expenses associated with computational analysis is a prominent issue for some of our clients.
Deloitte helped clients to address the following challenges:
Conducting a proof of concept to compare BigQuery editions with on-demand costsWhere to manage BigQuery editions slotsHow to charge back to different departmentsWhich criteria to use to group projects into reservationsHow to share idle slots from one reservation to others to reduce wasteHow many slots to commit for maximum ROI
Read on to learn how to address the above mentioned challenges as you work to optimize costs on Google Cloud with BigQuery.
First, if you are not familiar with BigQuery editions, we recommend that you readintroduction to BigQuery editions andintroduction to slots autoscaling.
Then, let’s understand the key differences between on-demand and BigQuery editions. In the on-demand pricing model, each project can scale up to 2,000 slots for analysis. The price is based on the number of bytes scanned multiplied by the unit price, independent of the slot capacity used.
On the other hand, BigQuery editions are billed based on slot hours. BigQuery editions allows for autoscaling, meaning it can scale up to the maximum number of slots defined and scale down to zero once computational analysis jobs are finished. Note that there is a one-minute scale-down window.
If you have workloads that require more than 2,000 slots per project available in on-demand, you should use BigQuery editions with higher capacity requirements. Additionally, if you’re using Enterprise or Enterprise Plus editions, you can assign baseline slots for workloads that are sensitive to “cold start” issues, ensuring consistent performance. Finally, you have the option to make a one- or three-year slot commitment to lower the unit price by 20% or 40%, respectively. Note: baseline and committed slots are charged 24/7, regardless of job activity.
Before creating a reservation, it’s essential to establish a BigQuery admin project within your organization dedicated solely to administering slots commitments and reservations. This project should not have any other workloads running inside it. By doing so, all slots charges are centralized in this project, streamlining administration.
There is value to managing all reservations in a single BigQuery admin project since idle and unallocated slots are only shared among reservations within the same administration project. This practice ensures efficient slot utilization and is considered a best practice.
To determine whether BigQuery editions slots are more cost-effective than on-demand for your workload, conduct a proof of concept by selecting a project with high on-demand query consumption and try out the BigQuery editions slots model. First, create a reservation within the BigQuery admin project and assign a project to it. Start with 2,000 slots as the maximum reservation size, equivalent to the current on-demand capacity.
You can then use the BigQuery administrative charts to determine slot cost. Additionally, you can run a query using the JOBS information schema to find out how many bytes have been scanned in the project to calculate the cost with the “on-demand” pricing model.
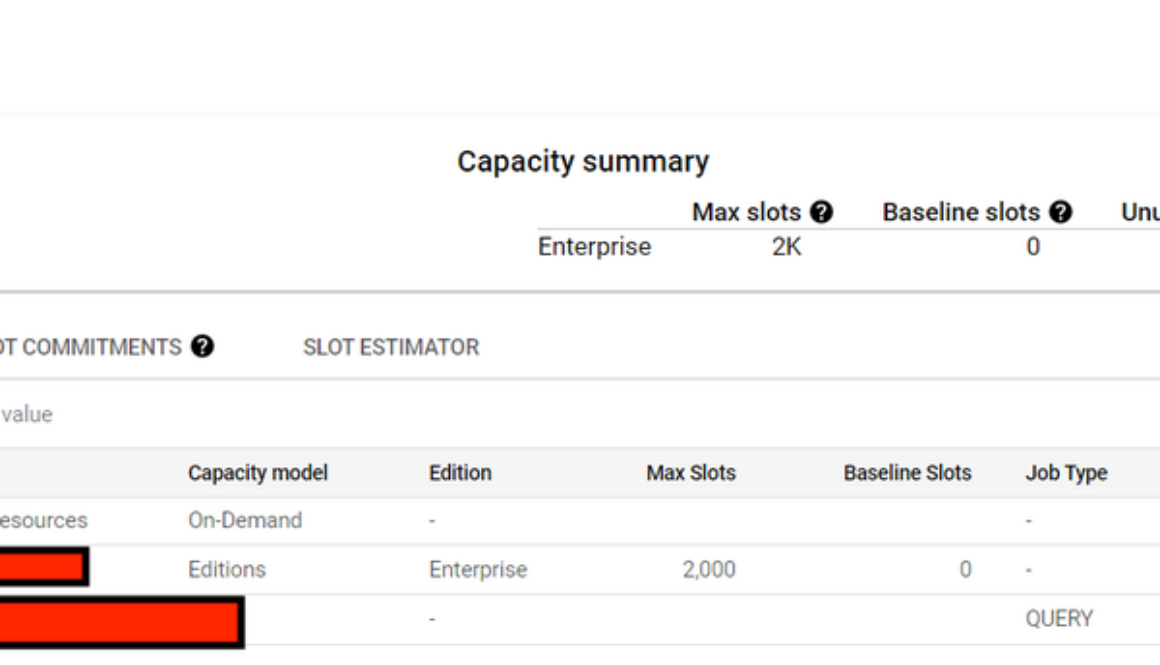
The following picture depicts a BigQuery slots reservation using Enterprise edition, with 2,000 max slots and 0 baseline slots without any commitment. Only one project has been assigned into this reservation to conduct a proof of concept:
Figure 1: Reservation with baseline and autoscaling slots.
Based on our experience, we saw huge benefits to leverage slots in our case. However, you must perform your own assessment as both slot-based and on-demand models offer value depending on your specific query requirements. For projects with minimal traffic volume and straightforward management needs, where most jobs or queries complete within seconds and data scans are limited, the on-demand model might be a more suitable choice.
Figure 2 and Figure 3 shows this comparison when using the BigQuery editions slot-cost model versus the on-demand model.
Figure 2: BigQuery editions slots costs.
From Figure 2, we see that the BigQuery editions slot cost is $1,641.
Figure 3: What-if using BigQuery on-demand costs.
Figure 3 shows a cost of $4,952 for the same time period when using BigQuery on-demand cost.
Figure 4 shows that the initial autoscaling slot size we used was too large. In Figure 7, you will see the recommended slot size from the slot estimator to allow you to reset the slot size for cost optimization.
Figure 4: The maximum number of auto-scaling slots is too large.
In the BigQuery editions slots model, all slot costs are recorded in the central BigQuery admin project. Chargeback to different departments becomes a crucial consideration when there are requirements to charge different departments or teams for resources consumed for billing and accounting purposes.
An upcoming BigQuery slot allocation billing report has lines for each reservation’s cost for each assigned query project. To facilitate chargeback, we recommend grouping projects based on their cost center, allowing for easy allocation. Until this new feature is available, you can run queries based on the BigQuery information schema to determine each project’s slot hours usage for chargeback purposes.
To optimize slot usage, consider grouping projects based on different workload types, such as Business Intelligence (BI), standard Extraction Transformation Loading (ETL), and data science projects. Each reservation can have unique characteristics shared by the group, defining baseline and maximum slots requirements. Grouping projects by cost center is an approach for efficient chargeback, with each cost center belonging to different departments (e.g., BI, ETL, data science).
Idle slots can be shared to avoid waste. By default, queries running in a reservation automatically use baseline idle slots from other reservations within the same administration project. Autoscaling slots are not considered idle capacity, as they are removed when they are no longer needed. Idle capacity is preemptible back to the original reservation as needed, irrespective of the query’s priority. This automatic and real-time sharing of idle slots helps to ensure optimal utilization.
Inintroduction to slots autoscaling, this picture explains a reservation with idle slots sharing;
Figure 5: Reservation with baseline, autoscaling slots and idle slots sharing.
Reservations use and add slots in the following priority:
Baseline slotsIdle slot sharing (if enabled)Autoscale slots
For the ETL reservation, the maximum number of slots possible is the sum of the ETL baseline slots (700) and the dashboard baseline slots (300, if all slots are idle), along with the maximum number of auto scale slots (600). Therefore, the ETL reservation in this example could utilize a maximum of 1600 slots.
By committing to a one- or three-year plan, you can get a 20% or 40% discount on pay-as-you-go slots (PAYG). However, if your workloads mainly consist of scheduled jobs and are not always running, you might end up paying for idle slots 24/7. To find the best reservation settings, you can use the slot estimator tool to analyze your usage patterns and gain insights. The tool suggests the optimal commitment level based on your usage. It uses a simulation starting with 100 slots as a unit to find the best ROI for your commitment level. The screenshot below shows an example of the tool.
Figure 6: Slot estimator for optimal cost settings.
Presently, the Google Cloud console also provides recommendations onorganization-level BigQuery editions in a dashboard, enabling you to gain a comprehensive overview of the entire system.
Figure 7 BigQuery editions Recommender Dashboard
Additionally, optimizing slots usage together with a 3-year commitment can further reduce costs.
Transitioning from on-demand ($/TB) to slots using BigQuery editions presents a significant opportunity for reducing analytics costs. By following the step-by-step guidance on conducting a proof of concept and transitioning to the BigQuery editions slots model, organizations can maximize their cost optimization efforts. We wish you a productive and successful cost optimization journey as you build with BigQuery! As always, reach out to us for support here.
Read More for the details.
The recent growth in distributed, compute-intensive ML applications has prompted data scientists and ML practitioners to find easy ways to prototype and develop their ML models. Running your Jupyter notebooks and JupyterHub on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) can provide a way to run your solution with security and scalability built-in as core elements of the platform.
GKE is a managed container orchestration service that provides a scalable and flexible platform for deploying and managing containerized applications. GKE abstracts away the underlying infrastructure, making it easy to deploy and manage complex deployments.
Jupyterhub is a powerful, multi-tenant server-based web application that allows users to interact with and collaborate on Jupyter notebooks. Users can create custom computing environments with custom images and computational resources in which to run their notebooks. “Zero to Jupyterhub for Kubernetes” (z2jh) is a Helm chart that you can use to install Jupyterhub on Kubernetes that provides numerous configurations for complex user scenarios.
We are excited to announce a solution template that will help you get started with Jupyterhub on GKE. This greatly simplifies the use of z2jh with GKE templates, offering a quick and easy way to set up Jupyterhub by providing a pre-configured GKE cluster, Jupyterhub config, and custom features. Further, we added features such as authentication and persistent storage and cut down the complexity for model prototyping and experimentation. In this blog post, we discuss the solution template, the Jupyterhub on GKE experience, unique characteristics that come from running on GKE, and features such as a custom authentication and persistent storage.
Running Zero to Jupyterhub on GKE provides a powerful platform for ML applications but the installation process is complicated. To ensure ML practitioners have minimal friction, our solution templates abstract away the infrastructure setup and solve common enterprise platform challenges including authentication and security, and persistent storage for notebooks.
Security and Auth
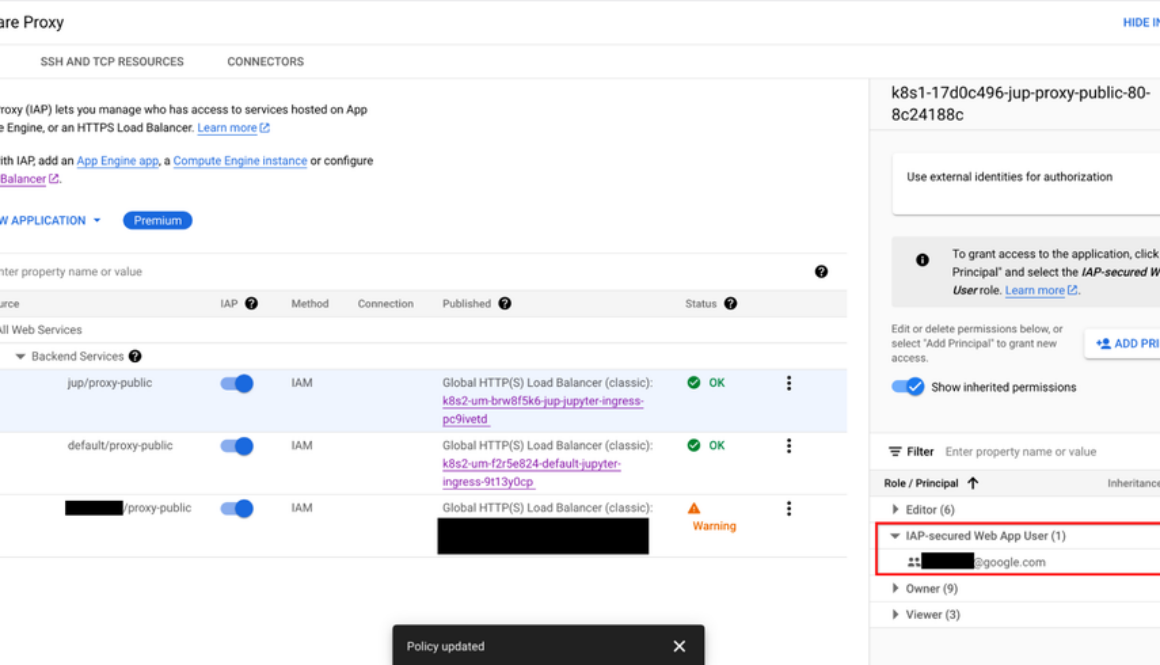
Granting the correct access to the notebooks can be especially difficult when working with sensitive data. By default, Jupyterhub exposes a public endpoint that anyone can access. This endpoint should be locked down to prevent unintended access. Our solution leverages Identity-Aware Proxy (IAP) to gate access to the public endpoint. IAP creates a central authorization layer for the Jupyterhub application access by HTTPS, utilizing the application-level access model and enabling IAM-based access control to the notebook to make users’ data more secure. Adding authentication to Jupyterhub ensures user validity and notebook security.
By default, the template reserves an IP address through Google Cloud IAP. Platform administrators can alternatively provide a domain to host their Jupyterhub endpoint, which will be guarded by IAP. Once IAP is configured, the platform administrator must update the service allowlist by granting users the role of “IAP-secure Web App User.” You can see how to allow access to the deployed Jupyterhub in the image below and as described here:
Now when a user navigates to the Jupyterhub endpoint gated behind IAP, they are presented with a Google login screen (shown below) to log in with their Google identity.
Persistent storage
Running Jupyterhub on GKE does not come with an out-of-the-box persistent storage solution, so notebooks are lost when the clusters are deleted. To persist notebook data, our templates provide options to integrate with Google storage solutions like Filestore, GCSFuse, andCompute Engine Persistent Disk. Each of these offer different features for different use cases:
Filestore – Supports dynamic provisioning and standard POSIX. Although the persistent volumes come with a minimum size of 1Ti for the standard tier, they provide multishare support to optimize costs.GCSFuse – Uses Cloud Storage buckets as the persistent volume but requires manual bucket creation i.e., the platform engineer must provision a bucket for each user. Cloud Storage can be managed via the UI support in the Google Cloud console and access control can be configured via IAM.Compute Engine Persistent Disk – Supports dynamic provisioning and can automatically scale while supporting different disk types.
To learn more about storage solutions, check out this guide.
The solution template uses Terraform with Helm charts to provision JupyterHub. Follow the step-by-step instructions in the README file to get started. The solution contains two groups of resources: platform-level and jupyterhub-level.
Platform-level resources are expected to be deployed once for each development environment by the system administrator. This includes common infrastructure and Google Cloud service integrations that are shared by all users. System administrators can also reuse already deployed development environments as well.
GKE Cluster and node pool – Configured in the main.tf file, this module deploys a GKE cluster with a GPU node pool. GKE also provides alternative GPU and machine types.Kubernetes System namespaces and service accounts, along with necessary IAM policy bindings.
The following resources are created when the system admins install Jupyterhub on the cluster. System administrators will be required to reinstall to apply any changes made to Jupyterhub configuration, i.e., the changes listed here.
Jupyterhub z2jh server – Spins up Jupyter notebook environments for users.IAP-related k8s deployments – This includes the Ingress, Backend Configuration, and Managed Certificate that integrates Google Cloud IAP with JupyterhubDepending on the user’s choice, storage volumes will be created by Filestore, GCSFuse, or Persistent Disk.
GKE’s flexible container customization and nodepool configurations work well with Jupyter’s concept of notebook profiles. Jupyterhub configuration offers a customizable number of preset profiles with predetermined Jupyter notebook images, memory, CPUs, GPUs, and many more. Using profiles, engineers can leverage GKE infrastructure like GPUs and TPUs to run their notebooks.
The combination of Jupyter and GKE offers a powerful yet simple solution for building, running, and managing AI workloads. Jupyterhub’s ease-of-use makes it a popular choice for machine learning models and data exploration. With GKE, Jupyterhub can go further by becoming more scalable and reliable.
You can also learn about running Jupyterhub with Ray here.
If you have any questions about using Jupyterhub with GKE, please raise an issue on our Github. Learn more about building AI Platforms with GKE by visiting our User Guide.
Read More for the details.

Students pursuing undergraduate degrees in engineering, computer science, IT, and other related fields: Are you curious about how to apply training and certifications to your real-life, day-to-day experience, or to upskill your technical capabilities? If so, this blog is for you.
In September and October 2023, approximately 100k students from 700 educational campuses in India completed the Google Cloud Computing Foundations course, learning generative AI skills that they can use on the job.
These students completed the course with help from learning content provided by Google Cloud Study Jams, community-led study groups run by Google Developer Student Clubs (GDSC). These study groups help aspiring developers get hands-on training in Google Cloud technologies, from containerizing applications to data engineering to machine learning and AI. They are set up as study parties, for a range of cloud topics and skill levels, and they can be tailored to group needs.
The study jam events in India had a significant impact for student learners and facilitators:
Students learned key foundational and technical skills to prepare them for their future careers.Student facilitators had the opportunity to gain a relevant Google Cloud certification.Nominated student facilitators gained leadership experience amongst their peers.
The Google Developer Student Clubs team in India started by reaching out to Google Cloud Developer Advocate Romin Irani to train student facilitators nominated from each GDSC educational institution. This train-the-trainer program focused on generative AI and cloud computing basics, and ran as a series of live sessions every week. The facilitators were then ready to manage the learning experience for students at their campuses.
In turn, student facilitators trained their students using learning material that is available to anyone, at any time. We encourage you to go check it out yourself. Materials included:
Google Cloud Computing Foundations: Cloud Computing Fundamentals – Comprised of videos, labs and quizzes, this introductory content helps learners gain hands-on skills in Google Cloud infrastructure, networking, security, data, and AI and ML.The Arcade – This no-cost gamified learning experience offers gen AI technical labs and the opportunity to earn swag. The games change from month to month, and must be completed within the month. The students in India worked on prompt engineering games.
Facilitators chose how they wanted to train their students. Some facilitators let students go through the training independently, acting merely as a point person for troubleshooting. Some taught the content digitally, and some in-person. Many facilitators took a hybrid approach.
Here’s what Himanshu Jagdale had to say about the facilitator experience:
“Being a Cloud Facilitator in Google Cloud Study Jams was a game-changer for my certification journey. It not only deepened my understanding of Google Cloud, but also allowed me to share knowledge, and collaborate with other facilitators who really helped me during my Associate Cloud Engineer certification. The hands-on labs and expert sessions by Romin Irani enriched my practical skills, making a significant contribution to my success in achieving the Google Cloud Associate Cloud Engineer certification.”
Participant Adarsh Rawat said:
“The Google Cloud Study Jam program was immensely beneficial to me. The hands-on labs and modules assisted me in building concepts and covering the certification syllabus. Honestly, I am a big fan of labs, as they allow for the coverage of most vital topics at once.”
If you’re a student with a passion for technology, we invite you to join a Google Developer Student Club near you — there are over 2100 Google Developer Student Clubs around the world, and joining one can help you learn, grow, and build a network of like-minded individuals, as well as find out about upcoming study jam opportunities. (If you’re not a student but looking to join a local community to stay connected and grow your skills, be sure to check out your local Google Developer Group.)
You can continue upskilling on Google Cloud by playing The Arcade at no-cost, with new games published regularly. Not only does The Arcade help you learn new hands-on technical skills, it also lets you gain points to use towards cool Google Cloud swag.
You can also visit Google Cloud Skills Boost for on-demand, role-based training to help you build your skills and validate your knowledge, any time, anywhere. You’ll find a variety of training options for in-demand job roles, like data analyst, security engineer, cloud engineer, machine learning engineer, and more, at levels ranging from introductory to advanced.
Start 2024 strong by upskilling with Google Cloud.
Read More for the details.
As Kubernetes adoption grows, so do the challenges of managing costs for medium and large-scale environments. The State of Kubernetes Cost Optimization report highlights a compelling trend: “Elite performers take advantage of cloud discounts 16.2x more than Low performers.”
There are probably lots of reasons for this, but a couple might be these teams’ in-house expertise, proficiency in overseeing large clusters, and targeted strategies that prioritize cost-efficiencies, including Spot VMs and committed use discounts (CUD). In this blog post, we list the best practices you can follow to create a cost-effective environment on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), and an overview of the top various cloud discounts available to GKE users.
Before selecting a cloud discount model to apply to your GKE environment, you need to know how much computing power your applications use, or you may end up overestimating your resource needs. You can do this by setting resource requests and rightsizing your workloads, helping to reduce costs and improve reliability. Alternatively, you can also create a VerticalPodAutoscaler (VPA) object to automate the analysis and adjustment of CPU and memory resources for Pods. And be sure to understand how VPA works before enabling it — it can either provide recommended resource values for manual updates or be configured to automatically update those values for your Pods.
GKE Autopilot shifts the mental model of Kubernetes cost optimization, in that you only pay for what resources your Pods request. But did you know that you can still take advantage of committed use on a per-Pod level? Reduce your GKE Autopilot costs with Kubernetes Engine (Autopilot Mode) committed use discounts. Autopilot Mode CUDs, which are based on one- and three-year commitments, can help you save 20% and 45% off on-demand prices, respectively. These discounts are measured in dollars per hour of equivalent on-demand spend. However, they do not cover GKE Standard, Spot pods, or management fees.
Flexible CUDs add flexibility to your spending capabilities by eliminating the need to restrict your commitments to a single project, region, or machine series. With Flexible CUDs, you can see a 28% discount over your committed hourly spend amount for a one-year commitment and 46% for a three-year commitment. With these spend-based commits, you can use vCPUs and/or memory in any of the projects within a Cloud Billing account, across any region, and that belong to any eligible general-purpose and/or compute-optimized machine type.
For GKE Standard, resources-based CUDs offer up to 37% off the on-demand prices for a one-year commitment, and up to 70% for a three-year commitment for memory-optimized workloads. GKE Standard CUDs cover only memory and vCPUs, and GPU commitments are subject to availability constraints. To guarantee that the hardware in your commit is available, we recommend you purchase commitments with attached reservations.
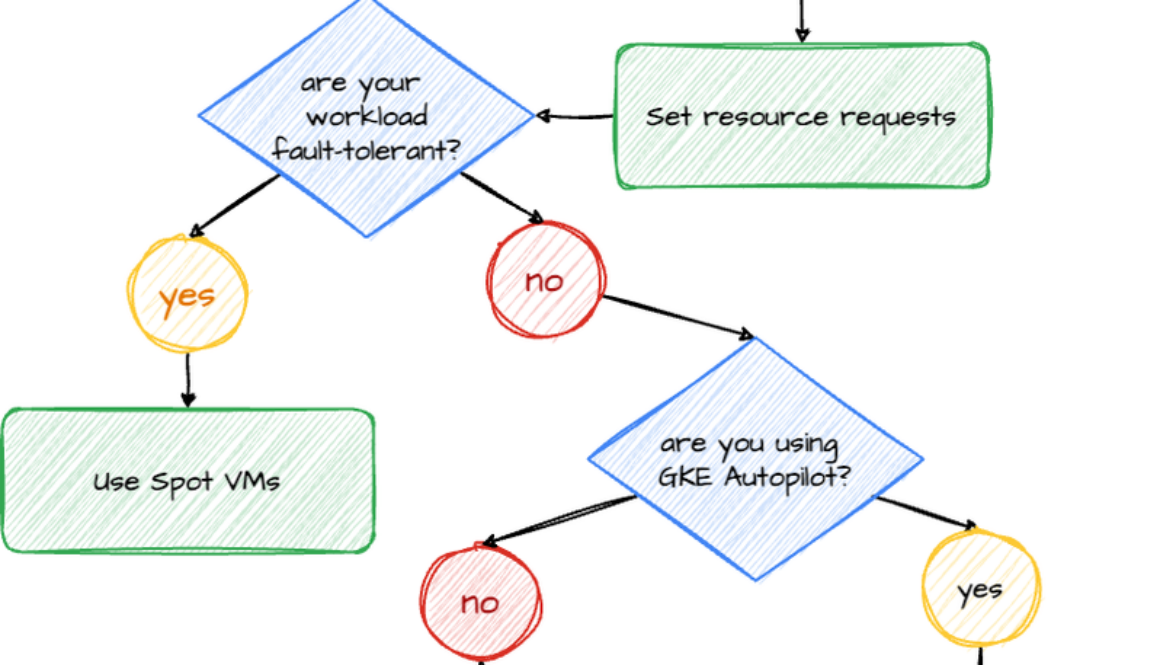
Here’s a bold statement: Spot VMs can reduce your compute costs by up to 91%. They offer the same machine types, options, and performance as regular compute instances. But the preemptible nature of Spot VMs means that they can be terminated at any time. Therefore, they’re ideal for stateless, short-running batch jobs, or fault-tolerant workloads. If your application exhibits fault tolerance (meaning it can shut down gracefully within 15 seconds and is resilient to possible instance preemptions), then Spot instances can significantly reduce your costs.
CUDs, meanwhile, also offer substantial cost savings for businesses that leverage cloud services. To maximize these savings, be sure to allocate resources strategically, ensure that workloads are appropriately sized, and employ optimization tools to assist in sizing your CUDs. By allocating resources efficiently, you can avoid unnecessary costs while maintaining consistent application performance. Adhere to the guidelines in this article to enjoy notable savings on your cloud services.
To determine when to use Spot VMs and when to choose CUD, check out the diagram below.
The State of Kubernetes Cost Optimization report talks about all these techniques in depth. Get your copy now, and now and dive deeper into the insights by exploring the series of blogs derived from this report:
Setting resource requests: the key to Kubernetes cost optimizationMaximizing Reliability, Minimizing Costs: Right-Sizing Kubernetes WorkloadsHow not to sacrifice user experience in pursuit of Kubernetes cost optimizationImprove Kubernetes cost and reliability with the new Policy Controller policy bundle
Read More for the details.
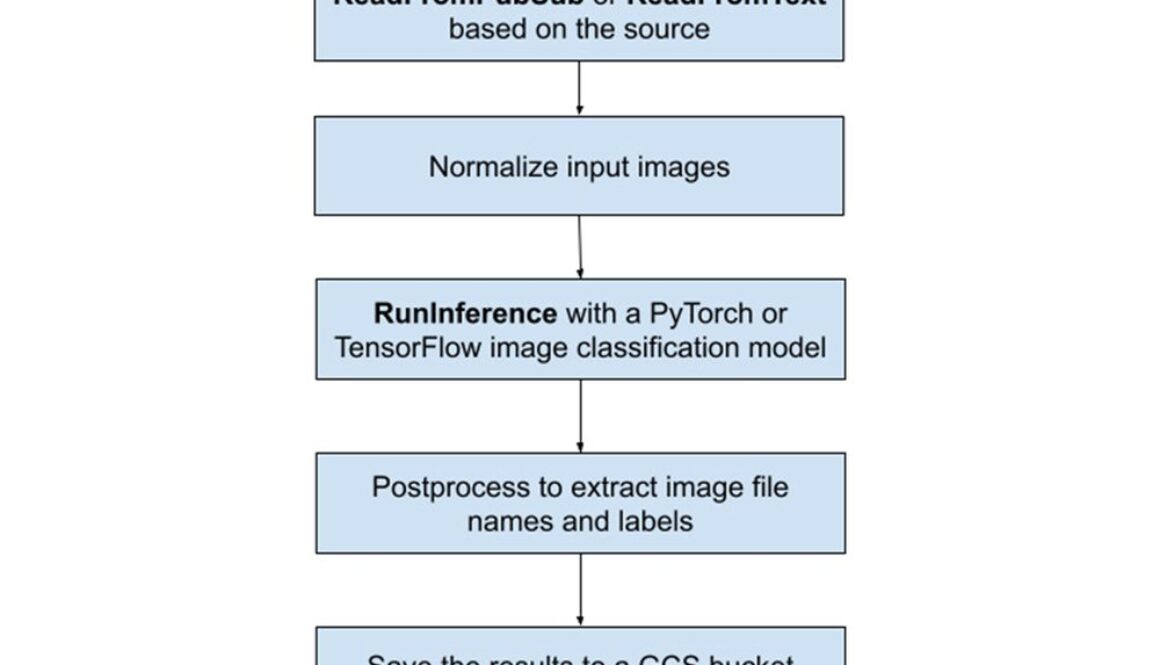
As part of BigQuery’s integrated suite of capabilities; Dataflow ML enables scalable local and remote inference with batch and streaming pipelines, as well as facilitating data preparation for model training and processing the results of model predictions. Our new Dataflow ML Starter project provides all of the essential scaffolding and boilerplate required to quickly and easily create and launch a Beam pipeline. In detail, the Dataflow ML Starter project contains a basic Beam RunInference pipeline that deploys some image classification models to classify the given images. As shown in Figure 1, The pipeline either reads the Cloud Storage (GCS) file that contains image GCS paths or subscribes a Pub/Sub source to receive image GCS paths, pre-processes the input images, runs a PyTorch or TensorFlow image classification model, post-processes the results, and finally writes all predictions back to the GCS output file.
The project illustrates the entire Dataflow ML development process by walking the user through each step, including:
Developing the Beam pipeline with a local Python environment and creating unit tests to validate the pipelineRunning the Beam RunInference job using DataflowRunner with CPUsImproving the inference speed and using GPUs, building and testing a custom container using GCE VMs and providing some Dockerfile samplesDemonstrating how to use Pub/Sub as the streaming source to classify imagesDemonstrating how to package all the code and apply a Dataflow Flex Template
In summary, the project produces a standard template that serves as a boilerplate, which can be easily modified to suit your specific needs.
To get started, visit the GitHub repository and follow the instructions. We believe that this starter project will be a valuable resource for anyone working with Dataflow ML. We are delighted to share our knowledge with the community and anticipate how it will help developers and data engineers achieve their goals. Please do not forget to star it if you find it helpful!
Read More for the details.
Data is increasingly valuable, powering critical dashboards, machine learning applications, and even large language models (LLMs). Conversely, that means every minute of data downtime — the period of time data is wrong, incomplete, or inaccessible — is more and more costly. For example, a data pipeline failure at a digital advertising platform company could result in hundreds of thousands in lost revenue .
Unfortunately, it is impossible to anticipate all the ways data can break with testing, and attempting to maintain a view of inconsistencies across your entire environment would be incredibly time-consuming.
Monte Carlo, a data observability software provider, together with Google Cloud can significantly minimize data downtime by utilizing cutting-edge Google Cloud services for ETL, data warehousing, and data analytics. Combined with the robust capabilities of Monte Carlo’s data observability, you can better detect, resolve, and prevent data incidents on a large scale.
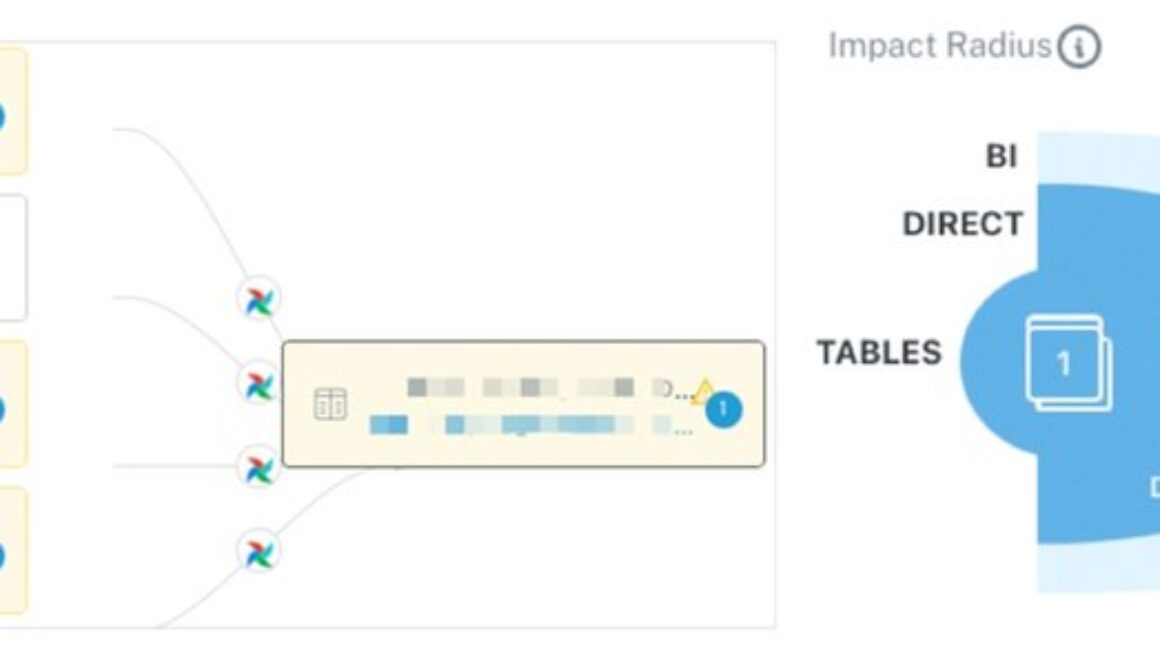
Monte Carlo’s data lineage shows the assets upstream with anomalies that may be related to the volume incident, while Impact Radius shows who will be affected to help inform smart triaging.
This is all enabled by the metadata, access to query logs, and other BigQuery features that help structure your data, as well as the APIs provided by Looker.
This reference architecture enables these key outcomes:
1. Mitigate the risk and impact of bad data: Reducing the number of incidents and improving time-to-resolution lowers the likelihood that bad data will cause negative reputational, competitive, and financial outcomes.
2. Increase data adoption, trust, and collaboration: Catching incidents first, and proactively communicating during the incident management process, helps build data trust and adoption. Data quality monitors and dashboards are the enforcement and visibility mechanisms required for creating effective, proactive data SLAs.
3. Reduce the time and resources spent on data quality: Studies show data teams average 30% or more of their workweek on data quality and other maintenance related tasks rather than tasks to unlock additional value from data and data infrastructure investments. Data observability reduces the amount of time data teams need to scale their data quality monitoring as well as resolving incidents.
4. Optimize the performance and cost of data products: When data teams move fast, they build “pipeline debt” over time. Slow-running data pipelines utilize excess compute, cause data quality issues, and create a poor user experience for data consumers, who must wait for data to return, dashboards to load, and AI models to update.
Monte Carlo recently expanded to a hybrid-SaaS offering using native Google Cloud technologies. The following diagram shows a Google-Cloud-hosted agent and datastore architecture for connecting BigQuery, Looker, and other data pipeline solutions to your Monte Carlo platform.
Additional architecture options include deployments where:
the MC agent is hosted within the Monte Carlo cloud environment and object storage remains as a Google Cloud Storage bucketboth the MC agent and object storage are hosted within the MC cloud environment
These deployment options help you choose how much control you want over your connection to the MC service as well as how you want to manage the agent/collector infrastructure.
The Google-Cloud-hosted agent and datastore option provides several capabilities, built on the following components:
Process and enrich data in BigQuery – BigQuery is a serverless and cost-effective enterprise data platform. Its architecture lets you use SQL language to query and enrich enterprise-scale data. And its scalable, distributed analysis engine lets you query terabytes in seconds and petabytes in minutes. Integrated ML and support for BI Engine lets you easily analyze the data and gain business insights.Visualize data and insights in Looker – Looker is a comprehensive business intelligence tool that consolidates your data via integration with numerous data sources. Looker lets users craft and personalize dashboards automatically, turning data into significant business metrics and dimensions. Linking Looker with BigQuery is straightforward, as users can add BigQuery projects and specific datasets directly as Looker data sources.Deploy the Monte Carlo agent and object storage – Monte Carlo uses an agent to connect to data warehouses, data lakes, BI and other ETL tools in order to extract metadata, logs and statistics. No record-level data is collected by the agent. However, there are times when Monte Carlo customers may want to sample a small subset of individual records within the platform as part of their troubleshooting or root-cause analysis process. Perhaps you need this type of sampling data to persist within your clouds, which can be done via dedicated object storage in Google Cloud Storage. To deploy the agent in your Google Cloud environment, you can access the appropriate infrastructure wrapper on the Terraform Registry. This launches a DockerHub image to Cloud Run for the agent and a Cloud Storage bucket for sampling data. The agent has a stable HTTPS endpoint that accesses the public internet and authorizes via Cloud IAM.Deploy object storage for Monte Carlo sampling data – There are times when Monte Carlo customers may want to sample a small subset of individual records within the platform for troubleshooting or to perform root-cause analysis process. They may have a desire or requirement for this type of sampling data to persist within their clouds, whether or not they choose to deploy and manage the Monte Carlo agent. Users can find the appropriate infrastructure wrapper available on the Terraform Registry (GitHub repository) that will generate the resourcesIntegrate Monte Carlo and BigQuery – Once the agent is deployed and you’ve established connectivity, you create a read-only service account with the appropriate permissions and provide the service credentials via the Monte Carlo onboarding wizard (details for BigQuery setup here). By parsing the metadata and query logs in BigQuery, Monte Carlo can automatically detect incidents and display end-to-end data lineage, all within days of deployment, without any additional configuration.Integrate Monte Carlo and Looker – You can also easily integrate Looker and Looker Git (formerly LookML code repository), which will allow Monte Carlo to map dependencies between Looker objects and other components of your modern data stack. This can be done by creating an API key on Looker that allows Monte Carlo to access metadata on your Dashboards, Looks, and other Looker Objects. You can then connect via private/public keys, which provides more granular control and connectivity, or HTTPS, which is recommended if you have many repos to connect to MC.Integrate Monte Carlo with Cloud Composer and Cloud Dataplex – The Monte Carlo agent can be effectively integrated with both Cloud Composer and Cloud Dataplex to enhance data reliability and observability across your Google Cloud data ecosystem. By integrating Monte Carlo with Cloud Composer and Cloud Dataplex, you can ensure enhanced data observability, quicker identification of data incidents, and more efficient root-cause analysis. This integration empowers teams to maintain high data quality and reliability across complex, multi-faceted data environments within Google Cloud.Integrate Monte Carlo and other ETL tools – Organizations’ data platforms often consist of multiple solutions to manage the data lifecycle — from ingestion, orchestration, and transformation, to discovery/access, visualization, and more. Depending on their size, some organizations may even use multiple solutions within the same category. For example, in addition to BigQuery, some organizations store and process data within other ETL tools powered by Google Cloud. Most of these integrations require a simple API key or service account to connect them to your Google-Cloud-hosted Monte Carlo agent. For more details on a specific integration, refer to Monte Carlo’s documentation.
In conclusion, deploying data observability with Monte Carlo and Google Cloud offers an invaluable solution to the increasingly critical issue of data downtime. By leveraging advanced Google Cloud services and Monte Carlo’s observability capabilities, organizations can not only mitigate risks associated with bad data but also enhance trust, collaboration, and efficiency across their data landscape. As we’ve explored, the integration of tools like BigQuery and Looker with Monte Carlo’s architecture creates a powerful synergy, optimizing data quality and performance while reducing the time and resources spent on data maintenance.
If you’re looking to elevate your organization’s data management strategies and minimize data downtime, consider exploring the integration of Monte Carlo with your Google Cloud environment. Start by evaluating your current data setup and identifying areas where Monte Carlo’s observability can bring immediate improvements. Remember, in the world of data, proactive management is key to unlocking its full potential.
Ready to take the next step? Reach out to the Monte Carlo or Google Cloud team today to begin your journey towards enhanced data observability and reliability. Let’s transform the way your organization handles data!
Read More for the details.

Businesses generate massive amounts of speech data every day, from customer calls to product demos to sales pitches. This data can transform your business by improving customer satisfaction, helping you prioritize product improvements and streamline business processes. While AI models have improved in the past few months, connecting speech data to these models in a scalable and governed way can be a challenge, and can limit the ability of customers to gain insights at scale.
Today, we are excited to announce the preview of Vertex AI transcription models in BigQuery. This new capability can make it easy to transcribe speech files and combine them with other structured data to build analytics and AI use cases — all through the simplicity and power of SQL, while providing built-in security and governance. Using Vertex AI capabilities, you can also tune transcription models to your data and use them from BigQuery.
Previously, customers built separate AI pipelines for transcription of speech data for developing analytics. These pipelines were siloed from BigQuery, and customers wrote custom infrastructure to bring the transcribed data to BigQuery for analysis. This helped to increase time to value, made governance challenging, and required teams to manage multiple systems for a given use case.
Google Cloud’s Speech to Text V2 API offers customers a variety of features to make transcription easy and efficient. One of these features is the ability to choose a specific domain model for transcription. This means that you can choose a model that is optimized for the type of audio you are transcribing, such as customer service calls, medical recordings, or universal speech. In addition to choosing a specialized model, you also have the flexibility to tune the model for your own data using model adaptation. This can allow you to improve the accuracy of transcriptions for your specific use case.
Once you’ve chosen a model, you can create object tables in BigQuery that map to the speech files stored in Cloud Storage. Object tables provide fine-grained access control, so users can only generate transcriptions for the speech files for which they are given access. Administrators can define row-level access policies on object tables and secure access to the underlying objects.
To generate transcriptions, simply register your off-the-shelf or adapted transcription model in BigQuery and invoke it over the object table using SQL. The transcriptions are returned as a text column in the BigQuery table. This process makes it easy to transcribe large volumes of audio data without having to worry about the underlying infrastructure. Additionally, the fine-grained access control provided by object tables ensures that customer data is secure.
Here is an example of how to use the Speech to Text V2 API with BigQuery:
This query generates transcriptions for all of the speech files in the object table and returns the results as a new text column named transcription.
Once you’ve transcribed the speech to text, there are three ways you can build analytics on the resulting text data:
Use BigQueryML to perform commonly used natural language use cases: BigQueryML provides wide running support to train and deploy text models. For example, you can use BigQuery ML to identify customer sentiment in support calls, or to classify product feedback into different categories. If you are a Python user, you can also use BigQuery Studio to run Pandas functions for text analysis.Join transcribed metadata, with other structured data stored in BigQuery tables: This allows you to combine structured and unstructured data for powerful use cases. For example, you could identify high customer lifetime value (CLTV) customers with negative support call sentiment, or shortlist the most requested product features from customer feedback.Call the PaLM API directly from BigQuery to summarize, classify, or prompt Q&A on transcribed data: PaLM is a powerful AI language model that can be used for a wide variety of natural language tasks. For example, you could use PaLM to generate summaries of support calls, or to classify customer feedback into different categories.
After transcription, you can unlock powerful search functionalities by building indexes optimized for needle-in-the-haystack queries, made possible by BigQuery’s search and indexing capabilities.
This integration also unlocks new generative LLM applications on audio files. You can use BigQuery’s powerful built-in ML functions to get further insights from the transcribed text, including ML.GENERATE_TEXT, ML.GENERATE_TEXT_EMBEDDING, ML.UNDERSTAND_TEXT, ML.TRANSLATE, etc., for various tasks like classification, sentiment analysis, entity extraction, extractive question answering, summarization, rewriting text in a different style, ad copy generation, concept ideation, embeddings and translation.
The above capabilities are now available in preview. Get started by following the documentation, demo, or contact your Google sales representative.
Read More for the details.

Cloud computing has become an essential part of many businesses and, as a Technical Account Manager, I have seen firsthand how cloud computing can help businesses save money and improve their agility. However, one of the challenges that businesses face when moving to the cloud is forecasting their cloud costs. If you are not careful, your cloud costs can quickly spiral out of control. That is where cloud cost forecasting comes in.
Cloud cost forecasting is essentially the process of predicting your future cloud usage. Forecasting is important in order to get funding, budget or support to start a new project in the cloud. Predicting your cloud costs can help you determine if you are on track with your FinOps strategy.
For many companies though, accurate cloud forecasting is one of the most difficult things to get right. In The State of Finops survey, advanced practitioners reported variances of about +/- 5% from their predictions – whilst less advanced reported variances as +/- 20%.
When I hear the word “forecasting,” I immediately think of weather predictions and, specifically, seasonality. For example, in the spring, you know that the weather will be milder than in the winter, and it is very unlikely to experience a snowstorm or a heatwave. You can predict things that are more likely to happen in spring since it is usually the rainiest season of the year.
If we apply this concept to cloud workloads, we will also discover seasons and events that will have a significant impact on cloud usage. For example, organizations may experience large spikes in demand during sales periods or year-end holidays. This will have a direct impact on consumption, which will result in additional costs. As a consequence, you will not only need to know your previous data to predict usage, but also the key factors that may influence your future consumption.
Ask yourself:
Does your business have seasonal peaks?Do you have any upcoming new projects, marketing events, or migrations planned that may result in additional users or consumption for your product?How often do you collate this data for future input into forecasting cycles?
The other key element in accurate forecasting is historical data. By analyzing your past usage, you can get a good idea of how your workloads are likely to change in the future. Historical data is key to determining costs in the future. This will help you to plan accordingly and avoid any unexpected costs. For example, if you see that your usage has been increasing steadily over the past few months as you are migrating your applications, you can expect it to continue to increase in the future. Additionally, if you see that your usage is fluctuating significantly, you may need to implement a more robust cost-management strategy.
Ask yourself:
Is my historical usage in-line with my defined seasonal peaks (if applicable?)Does my historical usage line up with expected business events?Did I appropriately investigate any forecast variations from my actuals? What were the results of variance analysis? Can I apply any lessons learned in my forecasting model?What’s my long-term trendline look like?
By understanding your historical data, you can make informed decisions about your future costs. TIP: In Google Cloud you can keep track of your consumption by exporting Cloud Billing data to BigQuery.
Now that you know your past data, and possible future events, you can start predicting your future cloud costs. There are a number of tools practitioners use to blend these two together, for example:
Your native cloud cost management tool (In GCP, that’s the GCP Billing console)Cost Estimation APIsSpreadsheetsMachine learning models using BQML or Vertex-AIThird-party forecasting tool
The best way to forecast depends on your specific needs and budget. If you have a small budget and are comfortable using spreadsheets, you can use that method. However, if you have a larger budget and need more accurate forecasts, you may want to consider using a cloud cost management tool or a third-party forecasting tool.
All things being equal, the out-of-the-box prediction feature in the Google Cloud Billing Console is a great place to start. The console provides an estimated cost for the current month based on your usage. This forecast is a combined total of actual cost to date and the projected cost trend. It is an approximation based on historical usage of all the projects that belong to that billing account. You can also adjust this forecast by filtering your report by project, service, sku, or folder in your organization.
Cloud forecasting is more manageable for a single project than for the entire organization. It is advised to forecast each project individually and then combine the forecasts to improve accuracy. The divide-and-conquer strategy is always a good approach to start small and end up with a very comprehensive forecast.
I was recently involved in a forecasting exercise for a retail customer to calculate their spending for the upcoming year. The customer did not have anything specific to predict their yearly commitment with Google Cloud for this reason we, the Google Cloud account team, worked and prepared a rough estimate of their future cloud costs.
One of the good things about this customer is that they were not new to GCP so we had several advantages to predict their costs:
We could get information from their historical dataWe knew their cloud journey and current maturity levelWe were also very familiar with their main workloadsAnd they shared with us their general plans for the following year
These were just a few advantages. On the other hand, since we didn’t know the details of each project, we couldn’t predict each project separately and combine all predictions later. As an alternative, we divided the spending and aggregated it by type of service: Compute Engine, GKE, Analytics, Networking, etc. In order to complete the estimate we followed the next steps:
Group all spending by service category (analytics, compute, networking, etc.)Calculate the average of the current and past two months’ spending for each service categoryCalculate the average of the same period from a year agoCompare the two averages to identify trends and assign each category its growth percentageFactor in all upcoming plans. Apply corrections for workloads that are stable, new, or intermittentShare the estimate with the customer and adapt it based on their feedback
The accuracy of our predictions can only be determined by the passage of time, there are always unforeseen factors that can affect the outcome of events. Only time will confirm how accurate our predictions are.
When forecasting your cloud costs, it’s important to be realistic. Don’t just assume that your costs will stay the same. Factor in changes in your cloud usage, changes in your cost drivers, and changes in the cloud market or pricing. Something that I have learned while helping my customers understand their cloud costs is that some products are used consistently, while others are used sporadically. For example, a product might be used heavily for one month and then not used at all for three months.
Lastly, cloud cost forecasting is an ongoing process that requires regular review and recalculation. Making small changes throughout the year will yield better results than waiting until the end of the year to make changes.
Now that you know how to forecast your future cloud costs, you can start tracking and monitoring your actuals versus your forecast and use variance analysis.
Read More for the details.
Want to know the latest from Google Cloud? Find it here in one handy location. Check back regularly for our newest updates, announcements, resources, events, learning opportunities, and more.
Tip: Not sure where to find what you’re looking for on the Google Cloud blog? Start here: Google Cloud blog 101: Full list of topics, links, and resources.
Announcing Launch of Cross Cloud Materialized Views: To help customers on their cross-cloud analytics journey, today we are thrilled to announce the public preview of BigQuery Omni cross-cloud materialized views (aka cross-cloud MVs). Cross-cloud MVs allow customers to very easily create a summary materialized view on GCP from base data assets available on another cloud. Cross-cloud MVs are automatically and incrementally maintained as base tables change, meaning only a minimal data transfer is necessary to keep the materialized view on GCP in sync. The result is an industry-first capability that empowers customers to perform frictionless, efficient, and cost-effective cross-cloud analytics
Google Cloud Global Cloud Service Provider of the Year. Google Cloud is thrilled to be recognized as Palo Alto Networks 2023 Global Cloud Service Provider of the Year and Global Cortex Partner of the Year. Google Cloud and Palo Alto Networks are dedicated to working together to support customer cloud journeys with an array of jointly engineered and integrated security solutions that enable digital innovation with ease. Read the Palo Alto Networks blog.GKE Enterprise edition free trial: We have announced the general availability of GKE Enterprise, the premium edition of Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) recently. With GKE Enterprise, companies can increase velocity across multiple teams, easily and securely run their most important business-critical apps and the latest AI/ML workloads safely at scale with a fully integrated and managed solution from Google Cloud. Start the 90-day free trial today with the GKE Enterprise edition by going to the GKE console and clicking on the “Learn about GKE Enterprise” button.Assured Workloads Resource ValidationIn our new blog post on Cost Management in BigQuery, you’ll learn how to use budgets and custom quota to help you stay on top of your spending and prevent surprises on your cloud bill. The interactive tutorials linked in the article will help you set them up for your own Google Cloud projects in no time!Leverage the transformative power of generative AI to elevate your customer service. Discover how you can optimize ROI, enhance customer satisfaction, and revolutionize your contact center operations with Google’s latest conversational AI offerings in this new blog.
In the first of our new Sketchnote series on Cloud FinOps, Erik and Pathik dive into what Cloud FinOps is, and how it can help your organization optimize its cloud budget.
Join Google Cloud’s product management leadership for a Data Analytics Innovation Roadmap session on November 13th. In this session, we will go through recent innovations, strategy and plans for BigQuery, Streaming Analytics, Data Lakes, Data Integration, and GenAI. This session will give you insight into Google’s feature development and will help your team plan your data analytics strategy.Hear from Google Cloud experts on modernizing software delivery with generative AI, running AI/ML workloads on GKE, the future of AI-infused apps, and more at Digital Transform: the future of AI-powered apps, November 15th.Vertex AI Search: Read about exciting new generative AI features coming to Vertex AI Search our platform to create search based applications for your business. Vertex AI Search provides customers with a tunable Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) system for information discovery. Learn more in this blog.Vector similarity search: If you are looking to build an an e ecommerce recommendations engine or ad serving or other DIY application based on ANN aka vector similarity search dive into our vector search capability which is a part of the Vertex AI Search platform. We’ve expanded features and made it easier then ever for developers to get started building their apps.Cloud Deploy – Deploy hooks (GA) allow users to specify and execute pre- and post- deploy actions using Cloud Deploy. This allows customers to run infrastructure deployment, database schema updates, and other activities immediately before a deploy job, and cleanup operations as part of a post (successful) deploy job. Learn MoreCloud Deploy – Cloud Deploy now uses Skaffold 2.8 as the default Skaffold version for all target types. Learn MoreArtifact Registry – Artifact Registry remote repositories are now generally available (GA). Remote repositories store artifacts from external sources such as Docker Hub or PyPI. A remote repository acts as a proxy for the external source so that you have more control over your external dependencies. Learn MoreArtifact Registry – Artifact Registry virtual repositories are now generally available (GA). Virtual repositories act as a single access point to download, install, or deploy artifacts in the same format from one or more upstream repositories. Learn More
ABAP SDK for Google Cloud now supports 40+ more APIs, an additional authentication mechanism and enhanced developer productivity for SAP ABAP developers. Learn more in this blog post.
Our newly published Storage decision tree helps you research and select the storage services in Google Cloud that best match your specific workload needs and the accompanying blog provides an overview of the services offered for block storage, object storage, NFS and Multi-Writer file storage, SMB storage, and storage for data lakes and data warehouses.
Meet the inaugural cohort of the Google for Startups Accelerator: AI First program featuring groundbreaking businesses from eight countries across Europe and Israel using AI and ML to solve complex problems. Learn how Google Cloud empowers these startups and check out the selected ventures here.BigQuery is introducing new SQL capabilities for improved analytics flexibility, data quality and security. Some examples include schema support for Flexible column name, Authorized store proceduces, ANY_VALUE (HAVING) also known as MAX_BY and MIN_BY and many more. Check out full details here.Cloud Logging is introducing to Preview the ability to save charts from Cloud Logging’s Log Analytics to a custom dashboard in Cloud Monitoring. Viewing, copying and sharing the dashboards are supported in Preview. For more information, see Save a chart to a custom dashboard.Cloud Logging now supports customizable dashboards in its Logs Dashboard. Now you, can add your own charts to see what’s most valuable to you on the Logs Dashboard. Learn more here.Cloud Logging launches several usability features for effective troubleshooting. Learn more in this blog post.Search your logs by service name with the new option in Cloud Logging. Now you can use the Log fields to select by service which makes it easier to quickly find your Kubernetes container logs. Check out the details here.Community Security Analytics (CSA) can now be deployed via Dataform to help you analyze your Google Cloud security logs. Dataform simplifies deploying and operating CSA on BigQuery, with significant performance gains and cost savings. Learn more why and how to deploy CSA with Dataform in this blog post.Dataplex data profiling and AutoDQ are powerful new features that can help organizations to improve their data quality and build more accurate and reliable insights and models. These features and now Generally Available. Read more in this blog post.
Introducing Looker’s Machine Learning Accelerator. This easy to install extension allows business users to train, evaluate, and predict with machine learning models right in the Looker interface.Learn about how Freestar has built a super low latency, globally distributed application powered by Memorystore and the Envoy proxy. This reference walks users through the finer details of architecture and configuration, that they can easily replicate for their own needs.
You can access comprehensive and up-to-date environmental information to develop sustainability solutions and help people adapt to the impacts of climate change through Google Maps Platform’s environment APIs. The Air Quality, and Solar APIs are generally available today. Get started or learn more in this blog post.Google Cloud’s Global Partner Ecosystems & Channels team launched the Industry Value Networks (IVN) initiative at Google Cloud NEXT ’23. IVNs combine expertise and offerings from systems integrators (SIs), independent software vendors (ISVs) and content partners to create comprehensive, differentiated, repeatable, and high-value solutions that accelerate time-to-value and reduce risk for customers. To learn more about the IVN initiative, please see this blog post
You can now easily export data from Earth Engine into BigQuery with our new connector. This feature allows for improved workflows and new analyses that combine geospatial raster and tabular data. This is the first step in toward deeper interoperability between the two platforms, supporting innovations in geospatial sustainability analytics. Learn more in this blog post or join our session at Cloud Next.
You can now view your log query results as a chart in the Log Analytics page in Cloud Logging. With this new capability available in Preview, users can write a SQL filter and then use the charting configuration to build a chart. For more information, see Chart query results with Log Analytics.
You can now use Network Analyzer and Recommender API to query the IP address utilization of your GCP subnets, to identify subnets that might be full or oversized. Learn more in a dedicated blog post here.Memorystore has introduced version support for Redis 7.0. Learn more about the included features and upgrade your instance today!
Attack Path Simulation is now generally available in Security Command Center Premium. This new threat prevention capability automatically analyzes a customer’s Google Cloud environment to discover attack pathways and generate attack exposure scores to prioritize security findings. Learn more. Get started now.
Cloud Deploy has updated the UI with the ability to Create a Pipeline along with a Release. The feature is now GA. Read moreOur newly published Data & Analytics decision tree helps you select the services on Google Cloud that best match your data workloads needs, and the accompanying blog provides an overview of the services offered for data ingestion, processing, storage, governance, and orchestration.Customer expectations from the ecommerce platforms are at all time high and they now demand a seamless shopping experience across platforms, channels and devices. Establishing a secure and user-friendly login platform can make it easier for users to self-identify and help retailers gain valuable insights into customer’s buying habits. Learn more about how they can better manage customer identities to support an engaging ecommerce user experience using Google Cloud Identity Platform.Our latest Cloud Economics post just dropped, exploring how customers can benchmark their IT spending against peers to optimize investments. Comparing metrics like tech spend as a percentage of revenue and OpEx uncovers opportunities to increase efficiency and business impact. This data-driven approach is especially powerful for customers undergoing transformation.
Cloud Deploy now supports deploy parameters. With deploy parameters you can pass parameters for your release, and those values are provided to the manifest or manifests before those manifests are applied to their respective target. A typical use for this would be to apply different values to manifests for different targets in a parallel deployment. Read moreCloud Deploy is now listed among other Google Cloud services which can be configured to meet Data Residency Requirements. Read moreLog Analytics in Cloud Logging now supports most regions. Users can now upgrade buckets to use Log Analytics in Singapore, Montréal, London, Tel Aviv and Mumbai. Read more for the full list of support regions.
Cloud CDN now supports private origin authentication in GA. This capability improves security by allowing only trusted connections to access the content on your private origins and preventing users from directly accessing it.Workload Manager – Guided Deployment Automation is now available in Public Preview, with initial support for SAP solutions. Learn how to configure and deploy SAP workloads directly from a guided user interface, leveraging end-to-end automation built on Terraform and Ansible.Artifact Registry – Artifact registry now supports clean up policies now in Preview. Cleanup policies help you manage artifacts by automatically deleting artifacts that you no longer need, while keeping artifacts that you want to store. Read more
Cloud Run jobs now supports long-running jobs. A single Cloud Run jobs task can now run for up to 24 hours. Read More.How Google Cloud NAT helped strengthen Macy’s security. Read more
Cloud Deploy parallel deployment is now generally available. You can deploy to a target that’s configured to represent multiple targets, and your application is deployed to those targets concurrently. Read More.Cloud Deploy canary deployment strategy is now generally available. A canary deployment is a progressive rollout of an application that splits traffic between an already-deployed version and a new version. Read More
Google Cloud’s Managed Service for Prometheus now supports Prometheus exemplars. Exemplars provide cross-signals correlation between your metrics and your traces so you can more easily pinpoint root cause issues surfaced in your monitoring operations.Managing logs across your organization is now easier with the general availability of user-managed service accounts. You can now choose your own service account when sending logs to a log bucket in a different project.Data Engineering and Analytics Day – Join Google Cloud experts on June 29th to learn about the latest data engineering trends and innovations, participate in hands-on labs, and learn best practices of Google Cloud’s data analytics tools. You will gain a deeper understanding of how to centralize, govern, secure, streamline, analyze, and use data for advanced use cases like ML processing and generative AI.
TMI: Shifting Down, Not Left- The first post in our new modernization series, The Modernization Imperative. Here, Richard Seroter talks about the strategy of ‘shifting down’ and relying on managed services to relieve burdens on developers.Cloud Econ 101: The first in a new series on optimizing cloud tools to achieve greater return on your cloud investments. Join us biweekly as we explore ways to streamline workloads, and explore successful cases of aligning technology goals to drive business value.The Public Preview: of Frontend Mutual TLS Support on Global External HTTPS Load Balancing is now available. Now you can use Global External HTTPS Load Balancing to offload Mutual TLS authentication for your workloads. This includes client mTLS for Apigee X Northbound Traffic using Global HTTPS Load Balancer.FinOps from the field: How to build a FinOps Roadmap – In a world where cloud services have become increasingly complex, how do you take advantage of the features, but without the nasty bill shock at the end? Learn how to build your own FinOps roadmap step by step, with helpful tips and tricks from FinOps workshops Google has completed with customers.We are now offering up to $1M of financial protection to help cover the costs of undetected cryptomining attacks. This is a new program only for Security Command Center Premium customers. Security Command Center makes Google Cloud a safe place for your applications and data. Read about this new program in our blog.Global External HTTP(S) Load Balancer and Cloud CDN’s advanced traffic management using flexible pattern matching is now GA. This allows you to use wildcards anywhere in your path matcher. You can use this to customize origin routing for different types of traffic, request and response behaviors, and caching policies. In addition, you can now use results from your pattern matching to rewrite the path that is sent to the origin.Security Command Center (SCC) Premium, our built-in security and risk management solution for Google Cloud, is now generally available for self-service activation for full customer organizations. Customers can get started with SCC in just a few clicks in the Google Cloud console. There is no commitment requirement, and pricing is based on a flexible pay-as-you-go model.Dataform is Generally Available. Dataform offers an end-to-end experience to develop, version control, and deploy SQL pipelines in BigQuery. Using a single web interface, data engineers and data analysts of all skill levels can build production-grade SQL pipelines in BigQuery while following software engineering best practices such as version control with Git, CI/CD, and code lifecycle management. Learn more.
Google Cloud Deploy. The price of an active delivery pipeline is reduced. Also, single-target delivery pipelines no longer incur a charge. Underlying service charges continue to apply. See Pricing Page for more details.
Security Command Center (SCC) Premium pricing for project-level activation is now 25% lower for customers who use SCC to secure Compute Engine, GKE-Autopilot, App Engine and Cloud SQL. Please see our updated rate card. Also, we have expanded the number of finding types available for project-level Premium activations to help make your environment more secure. Learn more.Vertex AI Embeddings for Text: Grounding LLMs made easy: Many people are now starting to think about how to bring Gen AI and large language models (LLMs) to production services. You may be wondering “How to integrate LLMs or AI chatbots with existing IT systems, databases and business data?”, “We have thousands of products. How can I let LLM memorize them all precisely?”, or “How to handle the hallucination issues in AI chatbots to build a reliable service?”. Here is a quick solution: grounding with embeddings and vector search. What is grounding? What are embedding and vector search? In this post, we will learn these crucial concepts to build reliable Gen AI services for enterprise use with live demos and source code.
Introducing the date/time selector in Log Analytics in Cloud Logging. You can now easily customize the date and time range of your queries in the Log Analytics page by using the same date/time-range selector used in Logs Explorer, Metrics Explorer and other Cloud Ops products. There are several time range options, such as preset times, custom start and end times, and relative time ranges. For more information, see Filter by time in the Log Analytics docs.Cloud Workstations is now GA. We are thrilled to announce the general availability of Cloud Workstations with a list of new enhanced features, providing fully managed integrated development environments (IDEs) on Google Cloud. Cloud Workstations enables faster developer onboarding and increased developer productivity while helping support your compliance requirements with an enhanced security posture. Learn More
Introducing BigQuery differential privacy, SQL building blocks that analysts and data scientists can use to anonymize their data. We are also partnering with Tumult Labs to help Google Cloud customers with their differential privacy implementations.Scalable electronic trading on Google Cloud: A business case with BidFX: Working with Google Cloud, BidFX has been able to develop and deploy a new product called Liquidity Provision Analytics (“LPA”), launching to production within roughly six months, to solve the transaction cost analysis challenge in an innovative way. LPA will be offering features such as skew detection for liquidity providers, execution time optimization, pricing comparison, top of book analysis and feedback to counterparties. Read more here.AWS EC2 VMs discovery and assessment – mFit can discover EC2 VMs inventory in your AWS region and collect guest level information from multiple VMs to provide technical fit assessment for modernization. See demo video.Generate assessment report in Microsoft Excel file – mFit can generate detailed assessment report in Microsoft Excel (XLSX) format which can handle large amounts of VMs in a single report (few 1000’s) which an HTML report might not be able to handle.Regulatory Reporting Platform: Regulatory reporting remains a challenge for financial services firms. We share our point of view on the main challenges and opportunities in our latest blog, accompanied by an infographic and a customer case study from ANZ Bank. We also wrote a white paper for anyone looking for a deeper dive into our Regulatory Reporting Platform.Google is partnering with regional carriers Chunghwa Telecom, Innove (subsidiary of Globe Group) and AT&T to deliver the TPU (Taiwan-Philippines-U.S.) cable system — connecting Taiwan, Philippines, Guam, and California — to support growing demand in the APAC region. We are committed to providing Google Cloud customers with a resilient, high-performing global network. NEC is the supplier, and the system is expected to be ready for service in 2025.
Microservices observability is now generally available for C++, Go and Java. This release includes a number of new features and improvements, making it easier than ever to monitor and troubleshoot your microservices applications. Learn more on our user guide.Google Cloud Deploy Google Cloud Deploy now supports Skaffold 2.3 as the default Skaffold version for all target types. Release Notes.Cloud Build You can now configure Cloud Build to continue executing a build even if specified steps fail. This feature is generally available. Learn more here
General Availability: Custom Modules for Security Health Analytics is now generally available. Author custom detective controls in Security Command Center using the new custom module capability.Next generation Confidential VM is now available in Private Preview with a Confidential Computing technology called AMD Secure Encrypted Virtualization-Secure Nested Paging (AMD SEV-SNP) on general purpose N2D machines. Confidential VMs with AMD SEV-SNP enabled builds upon memory encryption and adds new hardware-based security protections such as strong memory integrity, encrypted register state (thanks to AMD SEV-Encrypted State, SEV-ES), and hardware-rooted remote attestation. Sign up here!Selecting Tier_1 networking for your Compute Engine VM can give you the bandwidth you need for demanding workloads.Check out this blog on Increasing bandwidth to Compute Engine VMs with TIER_1 networking.
Use Terraform to manage Log Analytics in Cloud Logging You can now configure Log Analytics on Cloud Logging buckets and BigQuery linked datasets by using the following Terraform modules:Google_logging_project_bucket_configgoogle_logging_linked_dataset
Assured Open Source Software is generally available for Java and Python ecosystems. Assured OSS is offered at no charge and provides an opportunity for any organization that utilizes open source software to take advantage of Google’s expertise in securing open source dependencies.BigQuery change data capture (CDC) is now in public preview!
BigQuery CDC provides a fully-managed method of processing and applying streamed UPSERT and DELETE operations directly into BigQuery tables in real time through the BigQuery Storage Write API. This further enables the real-time replication of more classically transactional systems into BigQuery, which empowers cross functional analytics between OLTP and OLAP systems. Learn more here.
New Visualization tools for Compute Engine Fleets TheObservability tab in the Compute Engine console VM List page has reached General Availability. The new Observability tab is an easy way to monitor and troubleshoot the health of your fleet of VMsDatastream for BigQuery is Generally Available! Datastream for BigQuery is generally available, offering a unique, truly seamless and easy-to-use experience that enables near-real time insights in BigQuery with just a few steps. Using BigQuery’s newly developed change data capture (CDC) and Storage Write API’s UPSERT functionality, Datastream efficiently replicates updates directly from source systems into BigQuery tables in real-time. You no longer have to waste valuable resources building and managing complex data pipelines, self-managed staging tables, tricky DML merge logic, or manual conversion from database-specific data types into BigQuery data types. Just configure your source database, connection type, and destination in BigQuery and you’re all set. Datastream for BigQuery will backfill historical data and continuously replicate new changes as they happen.Now available! Build an analytics lakehouse on Google Cloud whitepaper. The analytics lakehouse combines the benefits of data lakes and data warehouses without the overhead of each. In this paper, we discuss the end-to-end architecture which enable organizations to extract data in real-time regardless of which cloud or datastore the data reside in, use the data in aggregate for greater insight and artificial intelligence (AI) – all with governance and unified access across teams. Download now.Now Available! Google Cloud Deploy now supports canary release as a deployment strategy. This feature is supported in Preview. Learn moreGeneral Availability : Cloud Run services as backends to Internal HTTP(S)Load Balancers and Regional External HTTP(S)Load Balancers. Internal load balancers allow you to establish private connectivity between Cloud Run services and other services and clients on Google Cloud, on-premises, or on other clouds. In addition you get custom domains, tools to migrate traffic from legacy services, Identity-aware proxy support, and more. Regional external load balancer, as the name suggests, is designed to reside in a single region and connect with workloads only in the same region, thus helps you meet your regionalization requirements. Learn more.
Last chance: Register to attend Google Data Cloud & AI Summit
Join us on Wednesday, March 29, at 9 AM PDT/12 PM EDT to discover how you can use data and AI to reveal opportunities to transform your business and make your data work smarter. Find out how organizations are using Google Cloud data and AI solutions to transform customer experiences, boost revenue, and reduce costs. Register today for this no cost digital event.New BigQuery editions: flexibility and predictability for your data cloud
At the Data Cloud & AI Summit, we announced BigQuery pricing editions—Standard, Enterprise and Enterprise Plus—that allow you to choose the right price-performance for individual workloads. Along with editions, we also announced autoscaling capabilities that ensure you only pay for the compute capacity you use, and a new compressed storage billing model that is designed to reduce your storage costs. Learn more about latest BigQuery innovations and register for the upcoming BigQuery roadmap session on April 5, 2023.Introducing Looker Modeler: A single source of truth for BI metrics
At the Data Cloud & AI Summit, we introduced a standalone metrics layer we call Looker Modeler, available in preview in Q2. With Looker Modeler, organizations can benefit from consistent governed metrics that define data relationships and progress against business priorities, and consume them in BI tools such as Connected Sheets, Looker Studio, Looker Studio Pro, Microsoft Power BI, Tableau, and ThoughtSpot.Cloud Workstations is now available in more regions. Cloud Workstations is now available in asia-south1 (India), us-east4 (Virginia, North America), europe-west6 (Switzerland), and europe-west9 (France). The full list of regions is here.Bucket based log based metrics—now generally available—allow you to track, visualize and alert on important logs in your cloud environment from many different projects or across the entire organization based on what logs are stored in a log bucket.NEW Customer Blog! Faced with strong data growth, Squarespace made the decision to move away from on-premises Hadoop to a cloud-managed solution for its data platform. Learn how they reduced the number of escalations by 87% with the analytics lakehouse on Google Cloud. Read now
Chronicle Security Operations Feature Roundup
Bringing a modern and unified security operations experience to our customers is and has been a top priority with the Google Chronicle team. We’re happy to show continuing innovation and even more valuable functionality. In our latest release roundup we’ll highlight a host of new capabilities focused on delivering improved context, collaboration, and speed to handle alerts faster and more effectively. Learn how our newest capabilities enable security teams to do more with less here.Announcing Google’s Data Cloud & AI Summit, March 29th!
Can your data work smarter? How can you use AI to unlock new opportunities? Join us on Wednesday, March 29, to gain expert insights, new solutions, and strategies to reveal opportunities hiding in your company’s data. Find out how organizations are using Google Cloud data and AI solutions to transform customer experiences, boost revenue, and reduce costs. Register today for this no cost digital event.Artifact Registry Feature Preview – Artifact Registry now supports immutable tags for Docker repositories. If you enable this setting, an image tag always points to the same image digest, including the default latest tag. This feature is in Preview. Learn more
Building the most open and innovative AI ecosystem
In addition to the news this week on AI products, Google Cloud has also announced new partnerships, programs, and resources. This includes bringing bringing the best of Google’s infrastructure, AI products, and foundation models to partners at every layer of the AI stack: chipmakers, companies building foundation models and AI platforms, technology partners enabling companies to develop and deploy machine learning (ML) models, app-builders solving customer use-cases with generative AI, and global services and consulting firms that help enterprise customers implement all of this technology at scale. Learn more.From Microbrows to Microservices
Ulta Beauty is building their digital store of the future, but to maintain control over their new modernized application they turned to Anthos and GKE – Google Cloud’s managed container services, to provide an eCommerce experience as beautiful as their guests. Read our blog to see how a newly-minted Cloud Architect learnt Kubernetes and Google Cloud to provide the best possible architecture for his developers. Learn more.To prepare for the busiest shopping season of the year, Black Friday and Cyber Monday, Lowe’s relies heavily on Google’s agile SRE Framework to ensure business and technical alignment, manage bots, and create an always-available shopping experience. Read more.Now generally available, understand and trust your data with Dataplex data lineage – a fully managed Dataplex capability that helps you understand how data is sourced and transformed within the organization. Dataplex data lineage automatically tracks data movement across BigQuery, BigLake, Cloud Data Fusion (Preview), and Cloud Composer (Preview), eliminating operational hassles around manual curation of lineage metadata. Learn more here.Rapidly expand the reach of Spanner databases with read-only replicas and zero-downtime moves. Configurable read-only replicas let you add read-only replicas to any Spanner instance to deliver low latency reads to clients in any geography. Alongside Spanner’s zero-downtime instance move service, you have the freedom to move your production Spanner instances from any configuration to another on the fly, with zero downtime, whether it’s regional, multi-regional, or a custom configuration with configurable read-only replicas. Learn more here.
Automatically blocking project SSH keys in Dataflow is now GA. This service option allows Dataflow users to prevent their Dataflow worker VMs from accepting SSH keys that are stored in project metadata, and results in improved security. Getting started is easy: enable the block-project-ssh-keys service option while submitting your Dataflow job.Celebrate International Women’s Day Learn about the leaders driving impact at Google Cloud and creating pathways for other women in their industries. Read more.Google Cloud Deploy now supports Parallel Deployment to GKE and Cloud Run workloads. This feature is in Preview. Read more.Sumitovant doubles medical research output in one year using Looker
Sumitovant is a leading biopharma research company that has doubled their research output in one year alone. By leveraging modern cloud data technologies, Sumitovant supports their globally distributed workforce of scientists to develop next generation therapies using Google Cloud’s Looker for trusted self-service data research. To learn more about Looker check out https://cloud.google.com/looker
Accelerate Queries on your BigLake Tables with Cached Metadata (Preview!)
Make your queries on BigLake Tables go faster by enabling metadata caching. Your queries will avoid expensive LIST operation for discovering files in the table and experience faster file and hive partition pruning. Follow the documentation here.Google Cloud Deploy support for deployment verification is now GA! Read more or Try the DemoAdd geospatial intelligence to your Retail use cases by leveraging the CARTO platform on top of your data in BigQuery
Location data will add a new dimension to your Retail use cases, like site selection, geomarketing, and logistics and supply chain optimization. Read more about the solution and various customer implementations in the CARTO for Retail Reference Guide, and see a demonstration in this blog.
Start your digital transformation by embarking on a hybrid cloud journey with Anthos. Anthos helps you modernize your application and infrastructure in place and build a unified Kubernetes fabric between your on prem environments and the Google cloud. The newly published Anthos hybrid cloud architecture reference design guide provides opinionated guidance to deploy Anthos in a hybrid environment to address some common challenges that you might encounter. Check out the architecture reference design guidehere to accelerate your journey to hybrid cloud and containerization.Logs for Network Load Balancingand logs for Internal TCP/UDP Load Balancingare now GA!
Logs are aggregated per-connection and exported in near real-time, providing useful information, such as 5-tuples of the connection, received bytes, and sent bytes, for troubleshooting and monitoring the pass-through Google Cloud Load Balancers. Further, customers can include additional optional fields, such as annotations for client-side and server-side GCE and GKE resources, to obtain richer telemetry.
Announcing Google’s Data Cloud & AI Summit, March 29th!
Can your data work smarter? How can you use AI to unlock new opportunities? Register for Google Data Cloud & AI Summit, a digital event for data and IT leaders, data professionals, developers, and more to explore the latest breakthroughs. Join us on Wednesday, March 29, to gain expert insights, new solutions, and strategies to reveal opportunities hiding in your company’s data. Find out how organizations are using Google Cloud data and AI solutions to transform customer experiences, boost revenue, and reduce costs. Register today for this no cost digital event.Leverege uses BigQuery as a key component of its data and analytics pipeline to deliver innovative IoT solutions at scale. As part of the Built with BigQuery program, this blog post goes into detail about Leverege IoT Stack that runs on Google Cloud to power business-critical enterprise IoT solutions at scale.Download white paper Three Actions Enterprise IT Leaders Can Take to Improve Software Supply Chain Security to learn how and why high-profile software supply chain attacks like SolarWinds and Log4j happened, the key lessons learned from these attacks, as well as actions you can take today to prevent similar attacks from happening to your organization.Running SAP workloads on Google Cloud? Upgrade to our newly released Agent for SAP to gain increased visibility into your infrastructure and application performance. The new agent consolidates several of our existing agents for SAP workloads, which means less time spent on installation and updates, and more time for making data-driven decisions. In addition, there is new optional functionality that powers exciting products like Workload Manager, a way to automatically scan your SAP workloads against best-practices. Learn how to install or upgrade the agent here.Deploy PyTorch models on Vertex AI in a few clicks with prebuilt PyTorch serving containers – which means less code, no need to write Dockerfiles, and faster time to production.Confidential GKE Nodes on Compute-Optimized C2D VMs are now GA. Confidential GKE Nodes help to increase the security of your GKE clusters by leveraging hardware to ensure your data is encrypted in memory, helping to defend against accidental data leakage, malicious administrators and “curious neighbors”. Getting started is easy, as your existing GKE workloads can run confidentially with no code changes required.
Immersive Stream for XR leverages Google Cloud GPUs to host, render, and stream high-quality photorealistic experiences to millions of mobile devices around the world, and is now generally available. Read more here.Reliable and consistent data presents an invaluable opportunity for organizations to innovate, make critical business decisions, and create differentiated customer experiences. But poor data quality can lead to inefficient processes and possible financial losses. Today we announce new Dataplex features: automatic data quality (AutoDQ) and data profiling, available in public preview. AutoDQ offers automated rule recommendations, built-in reporting, and serveless execution to construct high-quality data. Data profiling delivers richer insight into the data by identifying its common statistical characteristics. Learn more.Cloud Workstations now supports Customer Managed Encryption Keys (CMEK), which provides user encryption control over Cloud Workstation Persistent Disks. Read moreGoogle Cloud Deploy now supports Cloud Run targets in General Availability. Read moreLearn how to use NetApp Cloud Volumes Service as datastores for Google Cloud VMware Engine for expanding storage capacity. Read more
Oden Technologies uses BigQuery to provide real-time visibility, efficiency recommendations and resiliency in the face of network disruptions in manufacturing systems. As part of the Built with BigQuery program, this blog post describes the use cases, challenges, solution and solution architecture in great detail.Lytics is a next generation composable CDP that enables companies to deploy a scalable CDP around their existing data warehouse/lakes. As part of the Built with BigQuery program for ISVs, Lytics leverages Analytics Hub to launch secure data sharing and enrichment solution for media and advertisers. This blog post goes over Lytics Conductor on Google Cloud and its architecture in great detail.Now available in public preview, Dataplex business glossary offers users a cloud-native way to maintain and manage business terms and definitions for data governance, establishing consistent business language, improving trust in data, and enabling self-serve use of data. Learn more here.Security Command Center (SCC), Google Cloud’s native security and risk management solution, is now available via self-service to protect individual projects from cyber attacks. It’s never been easier to secure your Google Cloud resources with SCC. Read our blog to learn more. To get started today, go to Security Command Center in the Google Cloud console for your projects.Global External HTTP(S) Load Balancer andCloud CDN now support advanced traffic management using flexible pattern matching in public preview. This allows you to use wildcards anywhere in your path matcher. You can use this to customize origin routing for different types of traffic, request and response behaviors, and caching policies. In addition, you can now use results from your pattern matching to rewrite the path that is sent to the origin.Run large pods on GKE Autopilot with the Balanced compute class. When you need computing resources on the larger end of the spectrum, we’re excited that the Balanced compute class, which supports Pod resource sizes up to 222vCPU and 851GiB, is now GA!Manage table and column-level access permissions using attribute-based policies in Dataplex. Dataplex attribute store provides a unified place where you can create and organize a Data Class hierarchy to classify your distributed data and assign behaviors such as Table-ACLs and Column-ACLs to the classified data classes. Dataplex will propagate IAM-Roles to tables, across multiple Google Cloud projects, according to the attribute(s) assigned to them and a single, merged policy tag to columns according to the attribute(s) attached to them. Read more.
Starting with Anthos version 1.14, Google supports each Anthos minor version for 12 months after the initial release of the minor version, or until the release of the third subsequent minor version, whichever is longer. We plan to have Anthos minor release three times a year around the months of April, August, and December in 2023, with a monthly patch release (for example, z in version x.y.z) for supported minor versions. For more information, read here.Anthos Policy Controller enables the enforcement of fully programmable policies for your clusters across the environments. We are thrilled to announce the launch of our new built-in Policy Controller Dashboard, a powerful tool that makes it easy to manage and monitor the policy guardrails applied to your Fleet of clusters. New policy bundles are available to help audit your cluster resources against kubernetes standards, industry standards, or Google recommended best practices. The easiest way to get started with Anthos Policy Controller is to just install Policy controller and try applying a policy bundle to audit your fleet of clusters against a standard such as CIS benchmark.Dataproc is an important service in any data lake modernization effort. Many customers begin their journey to the cloud by migrating their Hadoop workloads to Dataproc and continue to modernize their solutions by incorporating the full suite of Google Cloud’s data offerings. Check out this guide that demonstrates how you can optimize Dataproc job stability, performance, and cost-effectiveness.Eventarc adds support for 85+ new direct events from the following Google services in Preview: API Gateway, Apigee Registry, BeyondCorp, Certificate Manager, Cloud Data Fusion, Cloud Functions, Cloud Memorystore for Memcached, Database Migration, Datastream, Eventarc, Workflows. This brings the total pre-integrated events offered in Eventarc to over 4000 events from 140+ Google services and third-party SaaS vendors.mFit 1.14.0 release adds support for JBoss and Apache workloads by including fit analysis and framework analytics for these workload types in the assessment report. See therelease notes for important bug fixes and enhancements.Google Cloud Deploy Google Cloud Deploy now supports Skaffold version 2.0. Release notesCloud Workstations – Labels can now be applied to Cloud Workstations resources. Release notesCloud Build – Cloud Build repositories (2nd gen) lets you easily create and manage repository connections, not only through Cloud Console but also through gcloud and the Cloud Build API. Release notes
Cloud CDN now supports private origin authentication for Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) buckets and compatible object stores in Preview. This capability improves security by allowing only trusted connections to access the content on your private origins and preventing users from directly accessing it.
Revionics partnered with Google Cloud to build a data-driven pricing platform for speed, scale and automation with BigQuery, Looker and more. As part of the Built with BigQuery program, this blog post describes the use cases, problems solved, solution architecture and key outcomes of hosting Revionics product, Platform Built for Change on Google Cloud.Pub/Sub Lite now offers export subscriptions to Pub/Sub. This new subscription type writes Lite messages directly to Pub/Sub – no code development or Dataflow jobs needed. Great for connecting disparate data pipelines and migration from Lite to Pub/Sub. See here for documentation.GPU Pods on GKE Autopilot are now generally available. Customers can now run ML training, inference, video encoding and all other workloads that need a GPU, with the convenience of GKE Autopilot’s fully-managed Kubernetes environment.Kubernetes v1.26 is now generally available on GKE. GKE customers can now take advantage of the many new features in this exciting release. This release continues Google Cloud’s goal of making Kubernetes releases available to Google customers within 30 days of the Kubernetes OSS release.Comprehensive guide for designing reliable infrastructure for your workloads in Google Cloud. The guide combines industry-leading reliability best practices with the knowledge and deep expertise of reliability engineers across Google. Understand the platform-level reliability capabilities of Google Cloud, the building blocks of reliability in Google Cloud and how these building blocks affect the availability of your cloud resources. Review guidelines for assessing the reliability requirements of your cloud workloads. Compare architectural options for deploying distributed and redundant resources across Google Cloud locations, and learn how to manage traffic and load for distributed deployments. Read the full blog here.
Read More for the details.

Welcome to the second Cloud CISO Perspectives for December 2023. To close out the year, I’m sharing what attracted the most interest from our security updates this year, and Nick Godfrey from our Office of the CISO presents a selection of forward-looking insights from the Office of the CISO and our new Cybersecurity Forecast report for 2024.
2023 was one of the rare years when an IT shift forever alters the world. While we’ve been using machine learning and AI in Google security for nearly two decades, the rise of generative AI dominated headlines and in our security updates. Below is a list of the top 10 security updates we’ve shared this year that garnered the most interest from our readers and customers.
As with all Cloud CISO Perspectives, the contents of this newsletter are posted to the Google Cloud blog. If you’re reading this on the website and you’d like to receive the email version, you can subscribe here.
Nick Godfrey, senior director, Office of the CISO
By Nick Godfrey, senior director, Office of the CISO
Cybersecurity can often seem like a reactive defensive scramble, hustling to respond to the latest zero-day vulnerability, treading water to stay above a churning sea of alerts, diving fast and deep into research, or madly dashing to keep business leaders and boards of directors appraised of security needs. However, proactive readiness is a key part of cybersecurity for an organization’s leaders, and our new Cybersecurity Forecast report uses today’s trends to explore likely scenarios that we expect to arise in the coming year.
The report was a collaborative effort across Google Cloud security teams, including Mandiant Intelligence, Mandiant Consulting, Chronicle Security Operations, Google Cloud’s Office of the CISO, and VirusTotal. Below we’ve highlighted a few key points from the report, bolstered with new insights from our Office of the CISO.
Generative AI drives defender conversations
We expect generative AI and foundation models to play a rapidly-growing role for threat actors and defenders alike. Threat actors will likely use AI to increase the scale of their information operations, and we expect to see “phishing, SMS, and other social engineering operations” that will appear more legitimate, we wrote in the report. AI will likely help them craft phishing attacks that contain fewer misspellings, grammar errors, and obviously- cultural context.
Yet as attackers get more persistent and innovative, cyber defenders will be able to tap into improved tools to stop them. Defenders will use gen AI and related technologies to strengthen detection, response, and attribution of adversaries at scale, as well as speed up analysis and other time-consuming tasks such as reverse engineering. In the long-term, we expect organizations using AI to boost security will see outsized benefits to reduce toil, address threat overload, and close the widening talent gap.
Marina Kaganovich, executive trust lead, Office of the CISO
Look for increasing instances of shadow AI in the workplace, when well-meaning employees use consumer-grade AI tools instead of more secure enterprise-grade counterparts. Since generative AI tools and use-cases will only mature over time, organizations should get ahead of the trend. They should develop plans to implement generative AI safely and successfully, and start by choosing gen AI tools that fit their use-cases.
Toby Scales, advisor, Office of the CISO
Companies involved in developing generative AI models will increasingly be held to account for errors or omissions in their models’ outputs, and enterprises who choose to adopt them will need to be aware of both the limits of foundational models and the emerging and unique methods to secure them. (For example, using open-source software tools such as Langchain and Rebuff.) As the pace of innovation increases, public declarations of AI principles and government-led efforts to guide responsible AI will become even more important as technical innovation and moral philosophy collide.
As CISOs become more accountable, so will the C-suite and boards
Taylor Lehmann, director, Office of the CISO
Following new SEC rules, we’ll see fewer CISOs accepting jobs without necessary job protections, like insurance and legal support, and clearly articulated board and senior leadership accountabilities for cybersecurity and risk management. The beliefs that the CISO is individually accountable for cybersecurity outcomes and that cybersecurity is beyond the typical responsibilities of non-technical leadership will no longer be accepted.
David Homovich, security consultant, Office of the CISO
In 2023, boards of directors across many industry verticals took a more active role in cybersecurity oversight, largely driven by the increased business risk associated with evolving threats and the potential impact of new regulations. This enhanced engagement reflects a growing recognition that cybersecurity is not just an IT issue, but a critical component of effective overall risk management practices. We’ll continue to encourage directors to get educated, be engaged, and stay informed to maintain effective oversight. Start planning now if you haven’t, particularly for budgeting and resourcing.
Expect more consolidation around SecOps
Anton Chuvakin, security advisor, Office of the CISO
Consolidation in security operations is a double-edged sword. While it promises efficiency and integration, it also risks vendor lock-in and stifling innovation. To help organizations avoid rigid platforms and siloed data, we want simpler tooling that works well and works with other tools. Preconfigured, opinionated workflows and detection content can jumpstart security programs and provide huge value to customers. However, to get the most of their detection and response tools, they need to go further.
This means treating content as a starting point, not a silver bullet:
Tailor vendor-provided content and workflows to your specific environment and threats.Invest in internal expertise and train your team to analyze threats, develop playbooks, and make informed decisions beyond vendor-provided content.Supplement vendor intelligence with diverse intelligence, including open-source threat feeds and threat research communities.
Attacks targeting hybrid and multicloud environments will have increasing impact
Jorge Blanco, director, Office of the CISO
During 2023, we saw elaborate attacks where attackers tried to overcome the boundaries between their target’s environments. The different technological strategies organizations use, including hybrid clouds, public-private clouds, and multicloud, are likely to complicate defending these environments.
We expect that identity-management problems and configuration errors, which currently account for the origin of more than half of today’s compromises, will continue to be the main entry vectors. Savvy organizations can reduce their risk with correct credential management, enforcing policies, and significant training dedicated to cloud environments and architectures specifically to avoid configuration errors.
Erin Joe, senior executive, cybersecurity, Office of the CISO
Nation-state and cyber-criminal threat actors are developing and using zero-day and publicly-known but unpatched vulnerabilities in record numbers to exploit edge devices and security appliances. These attack types are often not detected or detectable by traditional security approaches, such as firewalls or endpoint security appliances.
To combat these threats, security leaders should spend time in the coming year making sure their defense-in-depth strategies are broad and deep enough. They should work with business leaders to use automation and AI-boosted technologies to help modernize their security approach.
Collaboration and cybersecurity across the workplace
Odun Fadahunsi, Financial Services executive trust lead, Office of the CISO
In 2023, we brought together risk-management leaders responsible for overseeing cloud adoption, and hosted roundtable sessions for cloud adoption risk-management leaders. Cloud adoption risk, compliance, and control leaders can play a valuable role in 2024 by helping their organizations turn risk management results into a stronger driver of digital transformation goals.
Bill Reid, security consultant, Office of the CISO
This past year was a watershed moment for patient safety in medical devices. The FDA noted that without good cybersecurity, you cannot have a safe and effective medical device. A new law requires all new medical devices to incorporate secure-by-design practices, have strong ongoing vulnerability and patch management support, and provide a software bill of materials. This security work should align with the manufacturers’ quality management systems, which is important because we expect to see strong enforcement of the new rules.
Vinod D’Souza, head of manufacturing and industry, Office of the CISO
We’ll see supply chain vulnerabilities drive the conversation. Reliance on global suppliers and the continued convergence of interconnected systems are creating new attack surfaces that bad actors are using to compromise critical infrastructure and disrupt production. We are seeing this play out in multiple areas including in-vehicle hacking, smart energy grid vulnerabilities, operational technology exploitation, and industrial espionage that includes both intellectual property theft and competitor degradation. Customers should start developing plans to transform their security posture by leveraging cloud technologies and augmenting their capabilities with AI where it makes sense.
Here are the latest updates, products, services, and resources from our security teams so far this month:
Spotlighting ‘shadow AI’: How to protect against risky AI practices: The emerging trend of shadow AI, using consumer-grade AI in business settings, poses risks to organizations. Here’s why you should favor enterprise-grade AI. Read more.How European organizations are innovating with Google Sovereign Cloud solutions: Check out these examples of how Google’s Sovereign Cloud solutions have helped accelerate the adoption of breakthrough technologies like generative AI and data analytics. Read more.Introducing automated credential discovery to help secure your cloud environment: Google Cloud has launched — at no cost — a secret discovery tool in Sensitive Data Protection that can find and monitor for stored plaintext credentials. Read more.
Opening a can of whoop ads: How we disrupted a malvertising campaign: Earlier this year, Mandiant’s Managed Defense threat hunters identified a new malicious advertising campaign in sponsored search engine results and social media posts. Mandiant worked with the Google Anti-Malvertising team to remove the malicious advertisements from the ads ecosystem, and subsequently alerted other impacted organizations to also take action. Read more.FLOSS for Gophers and Crabs: Extracting strings from Go and Rust executables: The evolving landscape of software development has introduced new programming languages like Go and Rust. To support the static analysis of Go and Rust executables, FLOSS now extracts program strings using enhanced algorithms. Read more.Improving FLARE’s malware analysis tools at Google Summer of Code 2023: This summer marked the FLARE team’s first year participating in Google Summer of Code (GSoC), a global open-source software development mentoring program. Here’s an overview of the FLARE 2023 GSoC projects. Read more.
Kevin Mandia on cloud breaches: To close out the year, the CEO of Mandiant at Google Cloud joins hosts Anton Chuvakin and Tim Peacock to discuss new threat actors, old mistakes, and lessons for all. Listen here.
To have our Cloud CISO Perspectives post delivered twice a month to your inbox, sign up for our newsletter. We’ll be back in two weeks with more security-related updates from Google Cloud.
Read More for the details.
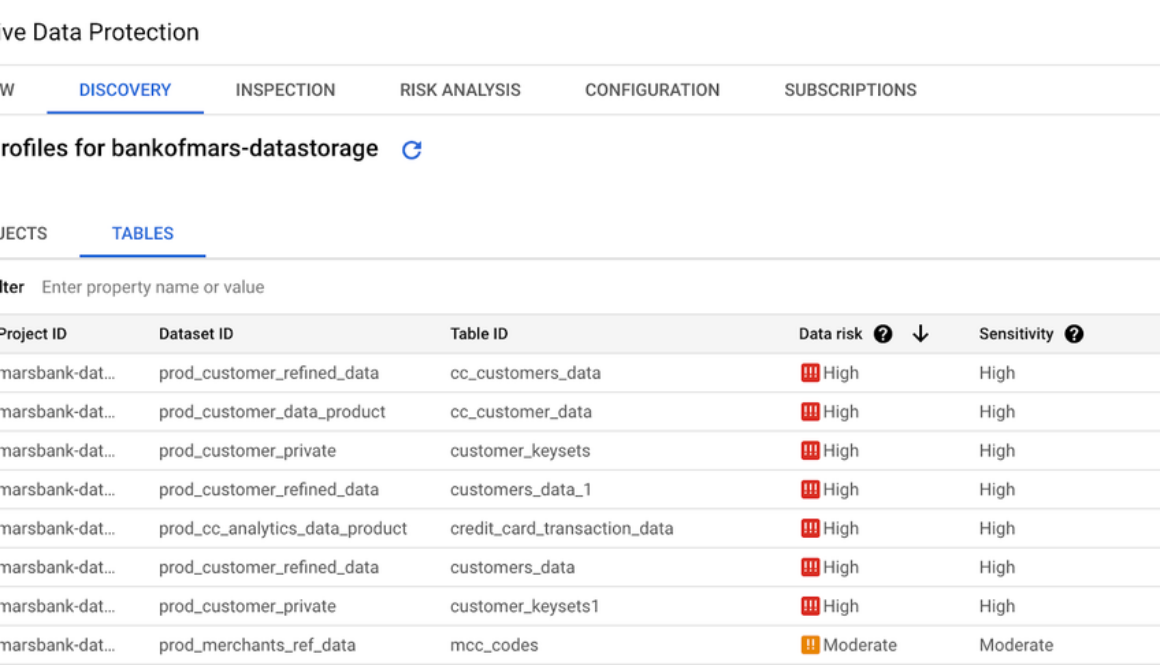
Editor’s note: Today we hear from global beauty brand, Charlotte Tilbury Beauty, on how they use Google Cloud Workflows and Sensitive Data Protection to respond quickly and at scale to customer data requests.
Launched in September 2013 by iconic beauty entrepreneur Charlotte Tilbury MBE, Charlotte Tilbury Beauty was born out of Charlotte’s long-held desire to empower everyone to feel like the most beautiful version of themselves, helping people around the world gain the confidence to achieve their biggest and boldest dreams.
Through Charlotte’s vision and leadership, at Charlotte Tilbury Beauty we continue to break records across regions, channels, and categories. We now sell more than 500 products across color, complexion, and skincare, we have a physical presence in over 50 global markets and 42 countries via charlottetilbury.com, as well as over 2,000 points of distribution worldwide including department stores and travel retail.
We are a customer-obsessed brand that strives to build a direct, emotional, and trusting relationship with our customers and partners. Our products and experiences are even better and more tailored to our customers when they choose to share their information with us, and trust us to appropriately redact and forget their information should they wish. Organizations that collect customer data have a responsibility to respond to customer data requests, be it a Right-To-Be-Forgotten (RTBF) or Data Subject Access Requests. Below, we focus on the data that resides on our Google infrastructure and explore how Google Cloud Workflows and Google Cloud Sensitive Data Protection (formerly Cloud Data Loss Prevention) have made it easier to respond to customer data deletion requests, and enabled our data team to develop an automated RTBF process.
To provide some context to the problem, our tool selection was driven by several needs and challenges:
A desire to have complete visibility over what, where, and how much PII is being stored in our Google Cloud environmentsData deletion from our data warehouse being heavily dependent on the deletion status in source systemsThe existing process being highly manual and unscalable for future volumes as well as having a limited audit trailA need for the solution to be independent from data warehouse processing workloadsA need for the solution to integrate with our consent management platform (OneTrust) whilst being able to perform complex BigQuery procedures and statementsThe language used in our product or marketing-specific content containing names that could be mistaken as PII
Google Cloud Sensitive Data Protection (SDP) provides us a way to scan the entirety of our BigQuery data and apply business-specific rules and edge cases to tune the performance of data profiling. This has significantly increased our understanding of our PII footprint, not just within our data warehouse but across the business. SDP scans for sensitive data at either daily, weekly, or monthly intervals, triggered by schema changes or changes in rows of data. These results, called data profiles, can be pushed to a number of destinations including Security Command Center, Chronicle, Dataplex, Pub/Sub, and BigQuery. In our case, we pushed to BigQuery for simplicity of consumption as part of our data deletion process.
As well as data discovery, SDP has the ability to encrypt and mask data based on the type of sensitive data identified.
Cloud Workflows gives us the ability to rapidly deploy a process that orchestrates multiple services in order to:
Retrieve the most recent open customer requestsScan our SDP data profiles for customer occurrencesApply business rules to determine the course of actionFulfill the deletion request via the BigQuery APIProvide a post-deletion report for manual checks
By using serverless infrastructure, we bypassed the burden of setting up development environments, SDKs, and API clients. This freed us to focus on meticulously defining and automating the data deletion request process through workflow YAML files and BigQuery SQL. Ultimately, Workflows fulfills the need to orchestrate and control the sequence of API requests to OneTrust, BigQuery (for routine execution and consuming SDP Data Profile results), and Cloud Functions (for processing of OneTrust API JSON response bodies), which allows us to automate a process that must consider dependencies between several systems.
The combination of Google SDP and Cloud Workflows provides simplicity to a complex problem. It has automated PII discovery in our BigQuery assets and has simplified the automation of data redaction through easy-to-define interactions with the BigQuery API and Consent Management System API. This approach has future-proofed our solution, where new data products or assets are automatically included in future SDP data profiles, and the redaction of the data product only requires a new BigQuery routine definition and a new routine invocation defined in the Workflow yaml.
It is worth mentioning that our infrastructure state is managed in Terraform Cloud, which means our automated deployments are made consistently in a declarative manner. There are still opportunities for continuous improvement, but these tools have given us a strong foundation on which to continue building trust with our customers when it comes to their data.
Read More for the details.
As part of our efforts to offer a best-in-class support experience, we launched Enhanced Support for Google Maps Platform in 2023. For customers with business-critical mapping workloads, Enhanced Support includes weekend coverage, escalations, communication with highly trained Google support engineers, and support for complex data issues.
“We’re happy to be able to now provide enterprise-grade support to organizations with mission-critical maps use cases,” says Jamie Erbes, Technical Customer Experience Director for Google Maps Platform.
Enhanced Support provides enterprise development teams with the responsive support they need to avoid impactful issues. With Enhanced Support, businesses get:
Responsiveness: 24/7 coverage, 365 days a year, including holidays, with a meaningful response within 1 hourExpertise: Advanced teams of highly trained support engineers respond to cases and communicate with customersQuota monitoring: Support engineers monitor your quota consumption, and increase your limits as needed, to avoid critical incidentsEscalation: Only Enhanced Support customers can escalate cases and receive high-level engineering support
We offer a seamless support experience for customers using both Google Cloud Platform and Google Maps Platform by aligning service level objectives and pricing. Google Maps Platform Enhanced Support is priced at $500/month + 3% of your Google Maps Platform monthly charges. Enhanced support customers can also:
Communicate with Google engineers via voice or video
Need to talk through an issue? Enhanced Support customers receive responsive communication from Google support engineers via voice or video, using Google Meet or the conferencing platform of your choice. We can pull in Google experts as needed to talk with your team and reach a resolution as quickly as possible.
Receive SLA incident reports
We keep our Enhanced Support customers informed during outages and provide follow-up Incident Reports that explain the impact, mitigation, and prevention steps, to help you enhance your application’s resilience.
Get help with map data quality issues
Enhanced Support customers receive individualized support for even the most complex requests; e.g., widespread systemic issues or situations where you don’t know the expected behavior. We’ll look into any issue you experience and swiftly escalate it to the correct team to investigate the quality of business-critical location data.
The value of Enhanced Support
Serious businesses need the enterprise-grade solutions provided by Google Maps Platform Enhanced Support. Contact your sales representative today or reach out to your Google Maps Platform or Partner point of contact to discuss Enhanced Support.
Standard Support is still available for customers who don’t require Enhanced Support. To determine which support level is right for your business, you can review the offerings in the chart below.
If your organization needs additional proactive assistance, ask your sales representative about our Developer Advisor Service, which provides API onboarding, implementation reviews, and additional proactive services.
Read More for the details.

Post Content
Read More for the details.

In today’s fast-changing marketing world, data is king. Marketers are under pressure to show solid returns on investment (ROI). With tightening budgets, marketers find themselves leaning heavily on data for strategic planning, audience targeting, performance evaluation, and efficient resource allocation.
As businesses strive to better understand their customers and deliver meaningful experiences, Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) have emerged as crucial tools in a marketer’s kit, enabling brands to build unified profiles of their customer data from all channels. They clean and standardize data across sources for easy integration with AdTech and MarTech platforms.
One pioneering CDP providing marketers with innovative and comprehensive customer solutions is Zeotap. By partnering with Google Cloud, and leveraging the same cloud technologies powering Search, YouTube, and Google Maps, Zeotap has built an intuitive marketers’ CDP.
As our collaboration redefines how brands manage and engage with customer data, this blog shows how Zeotap is leveraging Google’s generative AI prowess to enable marketers to derive even more value from their customer data by creating a CDP that is easy to use yet robust, drive deeper insights and marketing success.
Building effective and impactful marketing campaigns requires new ways to build deeper relationships with your customers while delivering results. For large brands, with multiple customer touch points, complex segmentation models are essential to provide context and time-based alerts and offers. However, these models can be difficult for non-technical users to understand and leverage effectively.
Ada™ Zeotap’s AI Companion is here to guide marketers through intuitive steps to build and analyze customer data to make insight-driven decisions. The seamless, accessible introduction enables all marketers, regardless of technical skill, to unlock valuable insights from their data. By simply conversing with Ada and describing their business goals and available data, marketers can effortlessly build custom segments that Ada will translate into actionable rules to review, save, or activate.
The foundation of this application lies atop Google’s Large Language model (LLM) PaLM2 on Vertex AI, which possesses an extensive understanding of human language and context. This model serves as the core component responsible for interpreting natural language commands. The deployment includes autonomous agents using this powerful LLM, serving as asynchronous threads of thought that coalesce together toward one common goal. Zeotap uses an ensemble [1] of such agents [2] called Mixture of Experts that work as a team to refine their ideas to provide a clear, straightforward response. Before taking any action, the automated assistants map out exactly what they plan to do using a method called ReAct [3].
When a user describes a segment to build, our system gathers the relevant catalog from internal data stores and aggregates it into a (JSON) LLM-readable format. After precise prompt tuning and elaborately crafted flows, we provide the AI with the user’s perceived intent, reference information, and plenty of sanity checks. Once the semantic intent is understood, the AI queries the metadata from the backing databases and identifies the relevant entities. Each of these entities is refined via a business context aware, exhaustive set of sanity checks through custom tailored heuristics to keep the agent’s hallucinations in check. Special care is taken to ensure that these processes do not change or interfere with the underlying client data.
Vertex AI’s Vector Search employs machine learning to grasp the essence and context of disorganized data. It relies on huge pre-trained models (text-embedding-gecko in this case) that have a broad range of knowledge and interpret meanings with great accuracy. These models can translate words, sentences, or paragraphs into numerical representations. These numerical representations encapsulate the root meaning, and as a result, similar numbers match similar ideas.
To break down the task into operators and values, we make two distinct requests to the Vertex AI’s LLM PaLM2 (text-bison) using the same basic information. Each request involves the context (user’s input), available values, and the previous agent’s response within the input. Because the pool of operators is limited, the AI Companion can consistently provide a reasonable response without needing further refinement. However, the actual answer may be wrong or missing. Additionally, the agent can only use a limited range of values and doesn’t understand columns with multiple possibilities. To address this, we compare Ada’s answer to the possible value for that column until we find a match using similarity search.
Once we have built these three structured groups, the primary role of PaLM-2 text-bison concludes. At this point, we employ these well-structured groups to construct SQL queries, which run using a designated client SQL Query Engine. We use this output to pre-fill the segment conditions which the user can verify and save the audience for activation.
Zeotap and Google Cloud are working together to transform how companies manage and engage with their clients. Our collaborative solutions are already driving value for Zeotap’s customers, offering an innovative, user-friendly interface that prioritizes simplicity and results. By harnessing the power of Google Cloud’s gen AI models, we are committed to making data-driven marketing more accessible and efficient.
Google’s generative AI technology has been instrumental in helping us unlock new possibilities for our customers. The synergy between Zeotap’s platform and Google’s advanced models has enabled us to deliver innovative solutions that improve accuracy, efficiency, and personalization. We are excited to continue collaborating with Google and exploring the potential of generative AI to transform the industry.
Our vision extends beyond audience refinement; we are dedicated to enhancing user experiences and pioneering innovative solutions. This involves streamlining data integration, automating data mapping, and equipping marketers with cutting-edge AI technology for effortless customer insights. In the upcoming months and years, Zeotap is committed to continuing our collaboration with Google Cloud to capitalize on all of the benefits that gen AI will bring to our customers.
Learn more about Google Cloud’s open and innovative generative AI partner ecosystem. Read more about Zeotap and Google Cloud.
Chen, Zixiang, et al. “Towards understanding mixture of experts in deep learning.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2208.02813 (2022).Karpas, Ehud, et al. “MRKL Systems: A modular, neuro-symbolic architecture that combines large language models, external knowledge sources and discrete reasoning.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.00445 (2022).Yao, Shunyu, et al. “React: Synergizing reasoning and acting in language models.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.03629 (2022).Ji, Bin. “VicunaNER: Zero/Few-shot Named Entity Recognition using Vicuna.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.03253 (2023).
Read More for the details.

If you’re considering using Vertex AI to train and deploy your models, you’re on the right track! Data is essential for machine learning, and the more data a model has and the higher quality it is, the better the model will perform. Before training a model, the data must be preprocessed, which means cleaning, transforming, and aggregating it into a format that the model can understand. Data preprocessing is also important when serving a model, but it can be more complex due to factors such as real-time streaming data, hardware scalability, and incomplete data.
When you’re handling large amounts of data, you need a service that’s both scalable and reliable. Dataflow fits the bill perfectly, as it can process data in both real-time and batch mode, and it’s ideal for models with high throughput and low latency requirements.
Dataflow and Vertex AI work great together, so keep reading to learn how to use these two powerful services to serve models for streaming prediction requests.
Use Case: Streaming Prediction Requests
Certain applications, such as anomaly detection in sensor data and predictive maintenance for industrial equipment, demand real-time predictions from machine learning models. Surprisingly, implementing real-time prediction systems doesn’t require an overly complex setup. If your machine learning model needs to make predictions on real-time data, a straightforward approach involves utilizing a Pub/Sub topic to capture real-time data, a Dataflow pipeline to preprocess and transform the data, and a Vertex AI endpoint to execute the machine learning model and generate predictions. Additionally, you can enable model monitoring to track any data or model changes that could impact prediction accuracy. The following diagram illustrates the workflow of this solution:
Deploy Model to Vertex AI Endpoint
First, we will need a trained model stored in Vertex AI Model Registry before the serving solution can be implemented. This can be done by either training a model in Vertex AI or importing a pre-trained model.
Now, with just a few clicks (or API calls), you can deploy your model to an endpoint in Vertex AI, so it can serve online predictions. You can enable model monitoring without writing any additional custom code, which helps ensure that there is no skew between the training and serving data.
Instead of deploying the model to an endpoint, you can use the RunInference API to serve machine learning models in your Apache Beam pipeline. This approach has several advantages, including flexibility and portability. However, deploying the model in Vertex AI offers many additional benefits, such as the platform’s built-in tools for model monitoring, TensorBoard, and model registry governance.
Vertex AI also provides the ability to use Optimized TensorFlow runtime in your endpoints. To do this, simply specify the TensorFlow runtime container when you deploy your model.
The Optimized TensorFlow runtime is a runtime that can improve the performance and cost of TensorFlow models. You can learn more about how to use it to speed up model inference here. This blog post contains benchmark data that shows how well it performs.
Data Processing Dataflow Pipeline
Apache Beam has built-in support for sending requests to a remotely deployed Vertex AI endpoint by using the VertexAIModelHandlerJSON class. With just a couple of lines of code, we can send the preprocessed message for inference.
Now, we’ll use Dataflow for the data preprocessing part. Below, you can find a code snippet of a python Apache Beam Pipeline which
1. Reads messages from Pub/Sub
2. Preprocesses the message. This can include the following:
a. Cleaning the data
b. Handling missing values
c. Encoding categorical data
d. Feature scaling
3. Sends a prediction request to the Vertex AI endpoint using the Vertex AI model handler
4. Processes the output. In this instance, we transform the raw output of the model into a format that is easily interpretable.
5. Write to BigQuery. Store the output in BigQuery so it can be easily retrieved.
What’s next?
The Apache Beam pipeline can be easily converted into a Flex Template, which allows multiple teams in the same company with similar use cases to reuse it. You can read more about flex templates here. Also, the Dataflow streaming pipeline can be run as one step of a Vertex AI Pipeline (take a look at some of the pre-built components).
In conclusion, Dataflow + Vertex AI is a powerful combination for serving machine learning models for both batch and streaming prediction requests. Dataflow can process data in both real-time and batch mode, and it’s ideal for use cases that require high throughput and low latency. Vertex AI provides a platform for deploying and managing models, and it also offers many additional benefits, such as built-in tools for model monitoring, the ability to leverage the Optimized Tensorflow Runtime, and Model Registry.
To learn more about how to use Dataflow and Vertex AI to serve machine learning models, please visit the following resource for detailed code samples: Apache Beam RunInference with Vertex AI.
Ready to discuss your cloud needs? Learn how Google Cloud Consulting can help you implement an end-to-end solution. Visit cloud.google.com/consulting.
Read More for the details.

Post Content
Read More for the details.